Structure Activity Relationships of α-L-LNA Modified Phosphorothioate Gapmer Antisense Oligonucleotides in Animals
- PMID: 23344239
- PMCID: PMC3499693
- DOI: 10.1038/mtna.2012.34
Structure Activity Relationships of α-L-LNA Modified Phosphorothioate Gapmer Antisense Oligonucleotides in Animals
Abstract
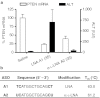
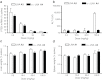
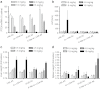
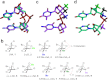
We report the structure activity relationships of short 14-mer phosphorothioate gapmer antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) modified with α-L-locked nucleic acid (LNA) and related modifications targeting phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN) messenger RNA in mice. α-L-LNA represents the α-anomer of enantio-LNA and modified oligonucleotides show LNA like binding affinity for complementary RNA. In contrast to sequence matched LNA gapmer ASOs which showed elevations in plasma alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels indicative of hepatotoxicity, gapmer ASOs modified with α-L-LNA and related analogs in the flanks showed potent downregulation of PTEN messenger RNA in liver tissue without producing elevations in plasma ALT levels. However, the α-L-LNA ASO showed a moderate dose-dependent increase in liver and spleen weights suggesting a higher propensity for immune stimulation. Interestingly, replacing α-L-LNA nucleotides in the 3'- and 5'-flanks with R-5'-Me-α-L-LNA but not R-6'-Me- or 3'-Me-α-L-LNA nucleotides, reversed the drug induced increase in organ weights. Examination of structural models of dinucleotide units suggested that the 5'-Me group increases steric bulk in close proximity to the phosphorothioate backbone or produces subtle changes in the backbone conformation which could interfere with recognition of the ASO by putative immune receptors. Our data suggests that introducing steric bulk at the 5'-position of the sugar-phosphate backbone could be a general strategy to mitigate the immunostimulatory profile of oligonucleotide drugs. In a clinical setting, proinflammatory effects manifest themselves as injection site reactions and flu-like symptoms. Thus, a mitigation of these effects could increase patient comfort and compliance when treated with ASOs.Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids (2012) 1, e47; doi:10.1038/mtna.2012.34; published online 18 September 2012.
Figures


References
-
- Bennett CF., and, Swayze EE. RNA targeting therapeutics: molecular mechanisms of antisense oligonucleotides as a therapeutic platform. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2010;50:259–293. - PubMed
-
- Swayze EE., and, Bhat B.2007The medicinal chemistry of oligonucleotides Crooke ST.ed). Antisense Drug Technology: Principles, Strategies, and Applications2nd edn. CRC Press: Boca Raton; 143–182.
-
- Altmann KH, Martin P, Dean NM., and, Monia BP. Second generation antisense oligonucleotides – inhibition of pkc-alpha and c-raf kinase expression by chimeric oligonucleotides incorporating 6'-substituted carbocyclic nucleosides and 2'-O-ethylene glycol substituted ribonucleosides. Nucleosides, Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids. 1997;16:917–926.
-
- Raal FJ, Santos RD, Blom DJ, Marais AD, Charng MJ, Cromwell WC.et al. (2010Mipomersen, an apolipoprotein B synthesis inhibitor, for lowering of LDL cholesterol concentrations in patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial Lancet 375998–1006. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

