p63 steps into the limelight: crucial roles in the suppression of tumorigenesis and metastasis
- PMID: 23344544
- PMCID: PMC4181578
- DOI: 10.1038/nrc3446
p63 steps into the limelight: crucial roles in the suppression of tumorigenesis and metastasis
Abstract
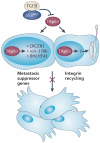
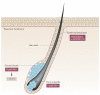
The role of p63 in cancer has been an area of intense debate and controversy. Is TP63 (which encodes p63) a tumour suppressor gene or an oncogene? This debate is partly due to the complexity of the gene. There are several p63 isoforms - some with tumour suppressive functions and others with oncogenic functions. In this Opinion article, we focus on the recent advances in understanding p63 biology and its roles in cancer. In this regard, we discuss the role of p63 in multiple stem cell compartments, ageing, in the response to DNA damage and in DNA repair. Finally, we highlight the importance of understanding the interactions between all three p53 family members and the potential impact of this knowledge on cancer therapy and regenerative medicine.
Figures


Similar articles
-
p63 is a suppressor of tumorigenesis and metastasis interacting with mutant p53.Cell Death Differ. 2011 Sep;18(9):1487-99. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2011.81. Epub 2011 Jul 15. Cell Death Differ. 2011. PMID: 21760596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of p63 in cancer, stem cells and cancer stem cells.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2011 Jun;16(2):296-327. doi: 10.2478/s11658-011-0009-9. Epub 2011 Mar 20. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2011. PMID: 21442444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p53/p63/p73 isoforms: an orchestra of isoforms to harmonise cell differentiation and response to stress.Cell Death Differ. 2006 Jun;13(6):962-72. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401914. Cell Death Differ. 2006. PMID: 16601753 Review.
-
P63 modulates the expression of the WDFY2 gene which is implicated in cancer regulation and limb development.Biosci Rep. 2019 Dec 20;39(12):BSR20192114. doi: 10.1042/BSR20192114. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31789342 Free PMC article.
-
The diverse oncogenic and tumour suppressor roles of p63 and p73 in cancer: a review by cancer site.Histol Histopathol. 2015 May;30(5):503-21. doi: 10.14670/HH-30.503. Epub 2014 Dec 16. Histol Histopathol. 2015. PMID: 25510918 Review.
Cited by
-
Ocular Manifestations in Patients Affected by p63-Associated Disorders: Ectrodactyly-Ectodermal Dysplasia-Clefting (EEC) and Ankyloblepharon-Ectodermal Defects-Cleft Lip Palate (AEC) Syndromes.J Clin Med. 2023 Nov 28;12(23):7377. doi: 10.3390/jcm12237377. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38068429 Free PMC article.
-
The function of Drosophila p53 isoforms in apoptosis.Cell Death Differ. 2015 Dec;22(12):2058-67. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.40. Epub 2015 Apr 17. Cell Death Differ. 2015. PMID: 25882045 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic control of meiosis surveillance mechanisms in mammals.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Feb 23;11:1127440. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1127440. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36910159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p63 and SOX2 Dictate Glucose Reliance and Metabolic Vulnerabilities in Squamous Cell Carcinomas.Cell Rep. 2019 Aug 13;28(7):1860-1878.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.07.027. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31412252 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus Gene BARF1 Expression is Regulated by the Epithelial Differentiation Factor ΔNp63α in Undifferentiated Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Mar 17;10(3):76. doi: 10.3390/cancers10030076. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29562599 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lane DP. Cancer p53, guardian of the genome. Nature. 1992;358:15–16. - PubMed
-
- Levine AJ, Hu W, Feng Z. The P53 pathway: what questions remain to be explored? Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:1027–1036. - PubMed
-
- Kaghad M, et al. Monoallelically expressed gene related to p53 at 1p36, a region frequently deleted in neuroblastoma and other human cancers. Cell. 1997;90:809–819. - PubMed
-
- Osada M, et al. Cloning and functional analysis of human p51, which structurally and functionally resembles p53. Nature Med. 1998;4:839–843. - PubMed
-
- Schmale H, Bamberger C. A novel protein with strong homology to the tumor suppressor p53. Oncogene. 1997;15:1363–1367. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

