Targeting DNA With Fingers and TALENs
- PMID: 23344620
- PMCID: PMC3381595
- DOI: 10.1038/mtna.2011.5
Targeting DNA With Fingers and TALENs
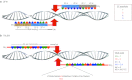
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

