Unique requirements for mono- and polyubiquitination of the peroxisomal targeting signal co-receptor, Pex20
- PMID: 23344950
- PMCID: PMC3591631
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.424911
Unique requirements for mono- and polyubiquitination of the peroxisomal targeting signal co-receptor, Pex20
Abstract
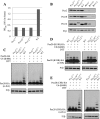
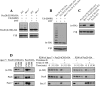
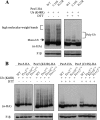
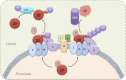
In Pichia pastoris, the peroxisomal targeting signal 2 (PTS2)-dependent peroxisomal matrix protein import pathway requires the receptor, Pex7, and its co-receptor Pex20. A conserved lysine (Lys(19)) near the N terminus of Pex20 is required for its polyubiquitination and proteasomal degradation, whereas a conserved cysteine (Cys(8)) is essential for its recycling. In this study, we found that Cys(8) is required for the DTT-sensitive mono- and diubiquitination of Pex20. We also show that the PTS2 cargo receptor, Pex7, is required for Pex20 polyubiquitination. Pex4, the E2 ubiquitin-conjugation enzyme, is required for monoubiquitination of Pex20. However, it is also necessary for polyubiquitination of Pex20, making its behavior distinct from the ubiquitination described for other PTS receptors. Unlike the roles of specific RING peroxins in Pex5 ubiquitination, we found that all the RING peroxins (Pex2, Pex10, and Pex12) are required as E3 ubiquitin ligases for Pex20 mono- and polyubiquitination. A model for Pex20 ubiquitination is proposed based on these observations. This is the first description of the complete ubiquitination pathway of Pex20, which provides a better understanding of the recycling and degradation of this PTS2 cargo co-receptor.
Figures





References
-
- Okumoto K., Misono S., Miyata N., Matsumoto Y., Mukai S., Fujiki Y. (2011) Cysteine ubiquitination of PTS1 receptor Pex5p regulates Pex5p recycling. Traffic 12, 1067–1083 - PubMed
-
- Honsho M., Hashiguchi Y., Ghaedi K., Fujiki Y. (2011) Interaction defect of the medium isoform of PTS1-receptor Pex5p with PTS2-receptor Pex7p abrogates the PTS2 protein import into peroxisomes in mammals. J. Biochem. 149, 203–210 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

