Treatment of splenic marginal zone lymphoma with rituximab monotherapy: progress report and comparison with splenectomy
- PMID: 23345547
- PMCID: PMC3579603
- DOI: 10.1634/theoncologist.2012-0251
Treatment of splenic marginal zone lymphoma with rituximab monotherapy: progress report and comparison with splenectomy
Abstract
Background: Treatment of splenic marginal zone lymphoma (SMZL) patients is not standardized. Recent data suggest that rituximab is highly effective and could be considered as initial therapy.
Aim: To assess the efficacy of rituximab monotherapy in a large series of patients with SMZL and compare these results with splenectomy results.
Methods: The studied population included 85 patients. Fifty-eight received rituximab at a dose of 375 mg/m2 per week for 6 weeks as induction followed by maintenance at the same dose every 2 months for 1-2 years, whereas 27 patients were treated using splenectomy only.
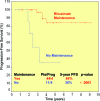
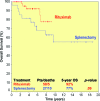
Results: The overall response rate to rituximab 2 months after the end of induction was 95% (complete response [CR], 45%; unconfirmed CR, 26%; partial response, 24%). The median times to hematologic and clinical response were 2 weeks and 3 weeks, respectively. Forty-three of 55 patients already completed the maintenance phase: 28 sustained their initial response, 14 improved their response, and one progressed. Eighty-five percent of splenectomized patients responded, and two were treated with rituximab as consolidation after splenectomy and achieved a CR. The 5-year overall and progression-free survival (PFS) rates for rituximab-treated and splenectomized patients were 92% and 77% (p = .09) and 73% and 58% (p = .06), respectively. Furthermore, maintenance therapy with rituximab resulted in a longer duration of response (at 5 years, PFS was 84% for patients receiving maintenance and 36% for patients without maintenance, p <.0001).
Conclusions: Rituximab is a very effective and well-tolerated therapy and may be substituted for splenectomy as the first-line treatment of choice for patients with SMZL.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures of potential conflicts of interest may be found at the end of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Armitage JO, Weisenburger DD. New approach to classifying non-Hodgkin's lymphomas: Clinical features of the major histologic subtypes. Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Classification Project. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16:2780–2795. - PubMed
-
- Isaacson PG, Piris MA, Berger F, et al. World Health Organization. Classification of Tumours: Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Lyon, France: IARC; 2008. Splenic B-cell marginal zone lymphoma; pp. 185–187.
-
- Matutes E, Oscier D, Montalban C, et al. Splenic marginal zone lymphoma proposals for a revision of diagnostic, staging and therapeutic criteria. Leukemia. 2008;22:487–495. - PubMed
-
- Matutes E, Morilla R, Owusu-Ankomach K, et al. The immunophenotype of splenic lymphoma with villous lymphocytes and its relevance to the differential diagnosis with other B-cell disorders. Blood. 1994;83:1558–1562. - PubMed
-
- Franco V, Florena ΑΜ, Iannitto Ε. Splenic marginal zone lymphoma. Blood. 2003;101:2464–2472. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

