Unusual patterns of IgG avidity in some young children following two doses of the adjuvanted pandemic H1N1 (2009) influenza virus vaccine
- PMID: 23345582
- PMCID: PMC3623405
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00619-12
Unusual patterns of IgG avidity in some young children following two doses of the adjuvanted pandemic H1N1 (2009) influenza virus vaccine
Abstract
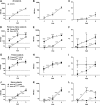
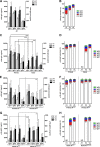
During the 2009-2010 H1N1 influenza pandemic, an adjuvanted monovalent vaccine containing ∼25% of the normal antigen dose and AS03 adjuvant was widely used in Canada. This vaccine was found to be well-tolerated and immunogenic in young children (D. W. Scheifele et al., Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 30:402-407, 2011). We report here additional analyses to further characterize the humoral response to this vaccine. We measured standard hemagglutination inhibition (HAI) and microneutralization (MN) titers, as well as influenza virus-specific IgG avidity and subclass distribution by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in 73 subjects. Sera were collected before (day 0) and 3 weeks after each dose of vaccine (days 21 and 42). Most children (55/73) had undetectable HAI and MN titers at day 0 (presumed to be antigen naive) and mounted good responses at days 21 and 42. The majority of these children (43/55) had the expected pattern of an increasing IgG avidity index (AI) after each dose of vaccine (not detected [ND], 0.30, and 2.97 at days 0, 21, and 42, respectively). The avidity responses in the remaining children (12/55) were quite different, with AIs increasing abruptly after the first dose and then declining after the second dose of vaccine (ND, 8.83, and 7.15, respectively). These children also had higher concentrations of influenza virus-specific IgG1 and IgG3 antibodies at day 21. Although the antibody titers were similar, some antigen-naive children demonstrated an unusual pattern of avidity maturation after two immunizations with AS03-adjuvanted, low-dose influenza virus vaccine. These data suggest the presence of subtle differences in the quality of the antibodies produced by some subjects in response to this vaccine.
Figures
References
-
- Leroux-Roels I, Borkowski A, Vanwolleghem T, Drame M, Clement F, Hons E, Devaster JM, Leroux-Roels G. 2007. Antigen sparing and cross-reactive immunity with an adjuvanted rH5N1 prototype pandemic influenza vaccine: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 370:580–589 - PubMed
-
- Levie K, Leroux-Roels I, Hoppenbrouwers K, Kervyn AD, Vandermeulen C, Forgus S, Leroux-Roels G, Pichon S, Kusters I. 2008. An adjuvanted, low-dose, pandemic influenza A (H5N1) vaccine candidate is safe, immunogenic, and induces cross-reactive immune responses in healthy adults. J. Infect. Dis. 198:642–649 - PubMed
-
- Technical Advisory Group on Vaccine-Preventable Diseases 2009. Final recommendations of pandemic influenza. Pan American Health Organization, Regional Office of the World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland: http://www.paho.org/english/ad/fch/im/PandemicFlu_TAGReco_Aug2009_e.pdf
-
- Morel S, Didierlaurent A, Bourguignon P, Delhaye S, Baras B, Jacob V, Planty C, Elouahabi A, Harvengt P, Carlsen H, Kielland A, Chomez P, Garcon N, Van MM. 2011. Adjuvant system AS03 containing alpha-tocopherol modulates innate immune response and leads to improved adaptive immunity. Vaccine 29:2461–2473 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

