Performance of the Elecsys Rubella IgG assay in the diagnostic laboratory setting for assessment of immune status
- PMID: 23345585
- PMCID: PMC3592356
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00688-12
Performance of the Elecsys Rubella IgG assay in the diagnostic laboratory setting for assessment of immune status
Abstract
Rubella in early pregnancy bears a high risk for congenital defects (e.g., cataracts, hearing loss, and heart disease) and for long-term sequelae in the newborn. Despite implementation of vaccination programs in many regions, the threat of devastating consequences from congenital rubella virus infection remains and careful screening of maternal immune status before and during pregnancy helps to reduce the risk. This study compared the performance of the Elecsys Rubella IgG assay with that of other assays routinely used for screening. Samples from 1,090 women undergoing routine antenatal care were tested using the Elecsys and Enzygnost Rubella IgG assays and the hemagglutination inhibition test. Samples with hemagglutination inhibition titers of <32 (n = 148) were additionally tested using the Vidas, AxSYM, Liaison, and Architect Rubella IgG assays. Agreement of qualitative results from the Elecsys, Enzygnost, and hemagglutination inhibition assays was good in all samples. All assays showed 100.0% specificity. In samples with hemagglutination inhibition titers of <32, the Elecsys, AxSYM, and Enzygnost assays showed higher sensitivity (>90.0%) than the other immunoassays (78.6 to 82.4%). The Elecsys assay reported significantly higher rubella virus IgG levels than the other immunoassays across the whole set of 1,090 samples, with the largest bias and deviation from limits of agreement in Bland-Altman analysis. In conclusion, the Elecsys assay is highly sensitive and specific with regard to qualitative results and suitable for routine automated screening. However, given the considerable variation between quantitative results from different immunoassays, testing methods should be documented and the same assay used throughout an individual's antenatal follow-up wherever possible.
Figures
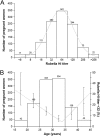


References
-
- Duszak RS. 2009. Congenital rubella syndrome—major review. Optometry 80:36–43 - PubMed
-
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence 2010. Antenatal care. Routine care for the healthy pregnant woman. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence, London, United Kingdom: http://www.nice.org.uk/nicemedia/pdf/CG062NICEguideline.pdf Accessed November 2012
-
- World Health Organization 2007. Manual for the laboratory diagnosis of measles and rubella virus infection. WHO/IVB/07.01, 2nd ed World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland: http://www.who.int/immunization_monitoring/LabManualFinal.pdf Accessed November 2012
-
- World Health Organization 2008. The immunological basis for immunization series. Module 11: rubella. http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2008/9789241596848_eng.pdf Accessed November 2012
-
- Australian Technical Advisory Group on Immunisation (ATAGI) 2008. The Australian immunisation handbook, 9th edition Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing, Canberra, Australia: http://www.health.gov.au/internet/immunise/publishing.nsf/Content/Handbo... Accessed January 2013
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

