A hepcidin lowering agent mobilizes iron for incorporation into red blood cells in an adenine-induced kidney disease model of anemia in rats
- PMID: 23345622
- PMCID: PMC3707526
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfs584
A hepcidin lowering agent mobilizes iron for incorporation into red blood cells in an adenine-induced kidney disease model of anemia in rats
Abstract
Background: Anemia is a common complication of chronic kidney disease (CKD) that negatively impacts the quality of life and is associated with numerous adverse outcomes. Excess levels of the iron regulatory hormone hepcidin are thought to contribute to anemia in CKD patients by decreasing iron availability from the diet and from body stores. Adenine treatment in rats has been proposed as an animal model of anemia of CKD with high hepcidin levels that mirrors the condition in human patients.
Methods: We developed a modified adenine-induced kidney disease model with a higher survival rate than previously reported models, while maintaining persistent kidney disease and anemia. We then tested whether the small molecule bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) inhibitor LDN-193189, which was previously shown to lower hepcidin levels in rodents, mobilized iron into the plasma and improved iron-restricted erythropoiesis in this model.
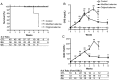
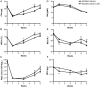
Results: Adenine-treated rats exhibited increased hepatic hepcidin mRNA, decreased serum iron, increased spleen iron content, low hemoglobin (Hb) and inappropriately low erythropoietin (EPO) levels relative to the degree of anemia. LDN-193189 administration to adenine-treated rats lowered hepatic hepcidin mRNA, mobilized stored iron into plasma and increased Hb content of reticulocytes.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that hepcidin lowering agents may provide a new therapeutic strategy to improve iron availability for erythropoiesis in CKD.
Keywords: anemia; chronic kidney disease; hepcidin; iron; mouse model.
Figures




References
-
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Anemia Work Group. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2012;2:279–335. doi:10.1038/kisup.2012.37. - DOI
-
- Besarab A, Coyne DW. Iron supplementation to treat anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2010;6:699–710. doi:10.1038/nrneph.2010.139. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Singh AK, Szczech L, Tang KL, et al. Correction of anemia with epoetin alfa in chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2085–2098. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa065485. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pfeffer MA, Burdmann EA, Chen CY, et al. A trial of darbepoetin alfa in type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:2019–2032. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0907845. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Besarab A, Bolton WK, Browne JK, et al. The effects of normal as compared with low hematocrit values in patients with cardiac disease who are receiving hemodialysis and epoetin. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:584–590. doi:10.1056/NEJM199808273390903. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

