Effects of a hybrid micro/nanorod topography-modified titanium implant on adhesion and osteogenic differentiation in rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- PMID: 23345973
- PMCID: PMC3548415
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S39357
Effects of a hybrid micro/nanorod topography-modified titanium implant on adhesion and osteogenic differentiation in rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Abstract
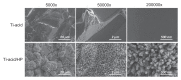
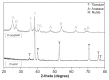
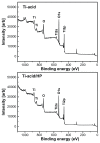
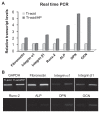
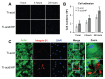
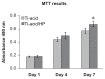
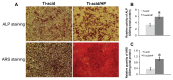
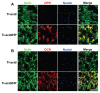
Background and methods: Various methods have been used to modify titanium implant surfaces with the aim of achieving better osseointegration. In this study, we fabricated a clustered nanorod structure on an acid-etched, microstructured titanium plate surface using hydrogen peroxide. We also evaluated biofunctionalization of the hybrid micro/nanorod topography on rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Scanning electron microscopy and x-ray diffraction were used to investigate the surface topography and phase composition of the modified titanium plate. Rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells were cultured and seeded on the plate. The adhesion ability of the cells was then assayed by cell counting at one, 4, and 24 hours after cell seeding, and expression of adhesion-related protein integrin β1 was detected by immunofluorescence. In addition, a polymerase chain reaction assay, alkaline phosphatase and Alizarin Red S staining assays, and osteopontin and osteocalcin immunofluorescence analyses were used to evaluate the osteogenic differentiation behavior of the cells.
Results: The hybrid micro/nanoscale texture formed on the titanium surface enhanced the initial adhesion activity of the rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Importantly, the hierarchical structure promoted osteogenic differentiation of these cells.
Conclusion: This study suggests that a hybrid micro/nanorod topography on a titanium surface fabricated by treatment with hydrogen peroxide followed by acid etching might facilitate osseointegration of a titanium implant in vivo.
Keywords: adhesion; bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; micro/nanotexture; nanorod; osteogenic differentiation; titanium surface.
Figures
References
-
- Wisbey A, Gregson P, Peter LM, Tuke M. Effect of surface treatment on the dissolution of titanium-based implant materials. Biomaterials. 1991;12(5):470–473. - PubMed
-
- Junker R, Dimakis A, Thoneick M, Jansen JA. Effects of implant surface coatings and composition on bone integration: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009;20(Suppl 4):185–206. - PubMed
-
- Lemons JE. Biomaterials, biomechanics, tissue healing, and immediate-function dental implants. J Oral Implantol. 2004;30(5):318–324. - PubMed
-
- Wennerberg A, Albrektsson T. Effects of titanium surface topography on bone integration: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009;20(Suppl 4):172–184. - PubMed
-
- Liu X, Chu PK, Ding C. Surface nano-functionalization of biomaterials. Mater Sci Eng R Rep. 2010;70(3):275–302.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

