Low dose aspirin therapy and renal function in elderly patients
- PMID: 23345988
- PMCID: PMC3549682
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S39065
Low dose aspirin therapy and renal function in elderly patients
Abstract
Purpose: To determine whether low dose aspirin has any deleterious effects on renal function in elderly patients.
Methods: We conducted a prospective pilot study of 30 Nigerians older than 60 years with various chronic ailments necessitating the use of low dose aspirin. Patients gave their consent, and institutional ethical clearance was obtained. Each patient's baseline samples at enrolment (before commencing aspirin use) served as a control, and subsequent weekly samples were compared. The weekly mean of each parameter was calculated, and the differences of means from baseline were determined, and values were compared for statistical differences with the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences, version 16.
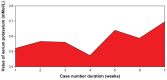
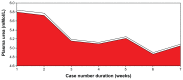
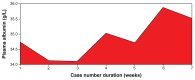
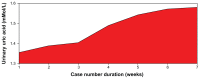
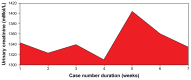
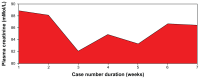
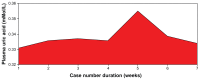
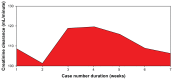
Results: We found that a majority of patients (86.67%) had basal renal functions at chronic kidney disease stages 1 and 2. When compared with the corresponding baseline parameters, the mean weekly serum and urinary electrolytes, urea, creatinine, and uric acid parameters did not change, and the P-value did not show any statistical significance. However, there was positive statistical significance for the creatinine clearance (P = 0.025). Also, unlike in previous studies, anemia and hypoalbuminemia did not affect the renal function parameters.
Conclusion: This study did not show any deleterious effects with short-term, low dose (75 mg daily) aspirin use on kidney functions in elderly patients. However, caution should be exercised when dealing with patients in renal stages 3-5 and the very elderly, aged ≥ 80 years.
Keywords: elderly; low dose aspirin; renal functions.
Figures
References
-
- Ancheta JI, Reding MJ. Stroke diagnosis and management: a multidisciplinary effort. In: Hazzard WR, Blass JP, Ettinger WH Jr, Halter JB, Ouslander JG, editors. Principles of Geriatric Medicine and Gerontology. 4th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1999. p. 124.
-
- Gurwitz JH, Gore JM, Goldberg RJ, Rubison M, Chandra N, Rogers WJ. Recent age-related trends in the use of thrombolytic therapy in patients who have had acute myocardial infarction. National Registry of Myocardial Infarction. Ann Intern Med. 1996;124(3):283–291. - PubMed
-
- Silagy CA, McNeil JJ, Donnan GA, Tonkin AM, Worsam B, Campion K. Adverse effects of low-dose aspirin in a healthy elderly population. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1993;54(1):84–89. - PubMed
-
- Krumholz HM, Radford MJ, Ellerbeck EF, et al. Aspirin in the treatment of acute myocardial infarction in elderly Medicare beneficiaries. Circulation. 1995;92(10):2841–2847. - PubMed
-
- Gurwitz JH, Avorn J, Ross-Degnan D, Lipsitz LA. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-associated azotemia in the very old. JAMA. 1990;264(4):471–475. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

