Tissue Doppler-derived E/e' ratio as a parameter for assessing diastolic heart failure and as a predictor of mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 23345995
- PMCID: PMC3543959
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2013.28.1.35
Tissue Doppler-derived E/e' ratio as a parameter for assessing diastolic heart failure and as a predictor of mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Background/aims: Diastolic dysfunction occurs frequently in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and is associated with heart failure (HF) or mortality. We investigated whether the ratio of early diastolic mitral inflow velocity to early diastolic mitral annulus velocity (E/e' ratio), estimated using tissue Doppler imaging, has prognostic value for cardiovascular morbidity and all-cause mortality in patients with CKD.
Methods: For 186 patients with CKD of stages III to V, we obtained echocardiograms with tissue Doppler imaging. A 5-year follow-up of 136 patients was performed based on hospital records and telephone interviews. The enrolled patients (79 males and 57 females) were categorized into the following CKD subgroups: stage III (n = 25); stage IV (n = 22); and stage V (n = 89).
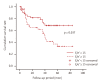
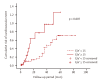
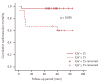
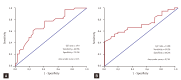
Results: The average follow-up period was 30.45 months and the mean age of the patients was 61.13 years. The mortality rate after 5 years was 60.0%. The causes of death were: sepsis, 21.9%; HF, 16.2%; and sudden death, 15.2%. Age (p = 0.000), increased C-reactive protein level (p = 0.018), and increased E/e' ratio (p = 0.048) were found to correlate with mortality. Age (p = 0.000), decreased ejection fraction (p = 0.003), and increased E/e' ratio (p = 0.045) correlated with cardiovascular event.
Conclusions: The E/e' ratio can predict mortality and cardiovascular events in patients with CKD who have diastolic dysfunction.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Diastolic heart failure; Echocardiography, Doppler; Mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article is reported.
Figures
Comment in
-
Diastolic dysfunction and chronic kidney disease.Korean J Intern Med. 2013 Jan;28(1):22-4. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2013.28.1.22. Epub 2012 Dec 28. Korean J Intern Med. 2013. PMID: 23345992 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Niizuma S, Iwanaga Y, Yahata T, et al. Impact of left ventricular end-diastolic wall stress on plasma B-type natriuretic peptide in heart failure with chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease. Clin Chem. 2009;55:1347–1353. - PubMed
-
- Sharp AS, Tapp RJ, Thom SA, et al. Tissue Doppler E/E' ratio is a powerful predictor of primary cardiac events in a hypertensive population: an ASCOT substudy. Eur Heart J. 2010;31:747–752. - PubMed
-
- Koprowski A, Gruchala M, Rynkiewicz A. Management of left ventricular diastolic heart failure: is it only blood pressure control? Curr Opin Cardiol. 2009;24:161–166. - PubMed
-
- Cerasola G, Nardi E, Palermo A, Mule G, Cottone S. Epidemiology and pathophysiology of left ventricular abnormalities in chronic kidney disease: a review. J Nephrol. 2011;24:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Hillis GS, Moller JE, Pellikka PA, et al. Noninvasive estimation of left ventricular filling pressure by E/e' is a powerful predictor of survival after acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43:360–367. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
