Lateralized interactive social content and valence processing within the human amygdala
- PMID: 23346054
- PMCID: PMC3548516
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2012.00358
Lateralized interactive social content and valence processing within the human amygdala
Abstract
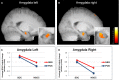
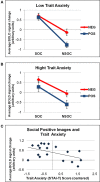
In the past, the amygdala has generally been conceptualized as a fear-processing module. Recently, however, it has been proposed to respond to all stimuli that are relevant with respect to the current needs, goals, and values of an individual. This raises the question of whether the human amygdala may differentiate between separate kinds of relevance. A distinction between emotional (vs. neutral) and social (vs. non-social) relevance is supported by previous studies showing that the human amygdala preferentially responds to both emotionally and socially significant information, and these factors might even display interactive encoding properties. However, no investigation has yet probed a full 2 (positive vs. negative valence) × 2 (social vs. non-social content) processing pattern, with neutral images as an additional baseline. Applying such an extended orthogonal factorial design, our fMRI study demonstrates that the human amygdala is (1) more strongly activated for neutral social vs. non-social information, (2) activated at a similar level when viewing social positive or negative images, but (3) displays a valence effect (negative vs. positive) for non-social images. In addition, this encoding pattern is not influenced by cognitive or behavioral emotion regulation mechanisms, and displays a hemispheric lateralization with more pronounced effects on the right side. Finally, the same valence × social content interaction was found in three additional cortical regions, namely the right fusiform gyrus, right anterior superior temporal gyrus, and medial orbitofrontal cortex. Overall, these findings suggest that valence and social content processing represent distinct kinds of relevance that interact within the human amygdala as well as in a more extensive cortical network, likely subserving a key role in relevance detection.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of emotion regulation strategy on brain responses to the valence and social content of visual scenes.Neuropsychologia. 2011 Apr;49(5):1067-1082. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2011.02.020. Epub 2011 Feb 21. Neuropsychologia. 2011. PMID: 21345342
-
Neural interaction of the amygdala with the prefrontal and temporal cortices in the processing of facial expressions as revealed by fMRI.J Cogn Neurosci. 2001 Nov 15;13(8):1035-47. doi: 10.1162/089892901753294338. J Cogn Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11784442
-
Neural correlates of successful emotional episodic encoding and retrieval: An SDM meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies.Neuropsychologia. 2020 Jun;143:107495. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2020.107495. Epub 2020 May 13. Neuropsychologia. 2020. PMID: 32416099
-
Distributed and interactive brain mechanisms during emotion face perception: evidence from functional neuroimaging.Neuropsychologia. 2007 Jan 7;45(1):174-94. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2006.06.003. Epub 2006 Jul 18. Neuropsychologia. 2007. PMID: 16854439 Review.
-
Social Regulation of Negative Valence Systems During Development.Front Syst Neurosci. 2022 Jan 20;15:828685. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2021.828685. eCollection 2021. Front Syst Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35126064 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Spatiotemporal pattern of appraising social and emotional relevance: Evidence from event-related brain potentials.Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2018 Dec;18(6):1172-1187. doi: 10.3758/s13415-018-0629-x. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30132268 Free PMC article.
-
Electrophysiological and behavioral evidence reveals the effects of trait anxiety on contingent attentional capture.Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2017 Oct;17(5):973-983. doi: 10.3758/s13415-017-0526-8. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28656503
-
Functional Neuroimaging of Adult-to-Adult Romantic Attachment Separation, Rejection, and Loss: A Systematic Review.J Clin Psychol Med Settings. 2021 Sep;28(3):637-648. doi: 10.1007/s10880-020-09757-x. Epub 2021 Jan 3. J Clin Psychol Med Settings. 2021. PMID: 33392890
-
Temporal Lobectomy Evidence for the Role of the Amygdala in Early Emotional Face and Body Processing.eNeuro. 2025 Feb 14;12(2):ENEURO.0114-24.2024. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0114-24.2024. Print 2025 Feb. eNeuro. 2025. PMID: 39890458 Free PMC article.
-
Working Memory-Related Prefrontal Hemodynamic Responses in University Students: A Correlation Study of Subjective Well-Being and Lifestyle Habits.Front Behav Neurosci. 2019 Sep 13;13:213. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2019.00213. eCollection 2019. Front Behav Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31572144 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aiken L. S., West S. G. (1991). Multiple Regression: Testing and Interpreting Interactions. Newbury Park, CA: Sage
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

