Neural dynamics of audiovisual synchrony and asynchrony perception in 6-month-old infants
- PMID: 23346071
- PMCID: PMC3549545
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00002
Neural dynamics of audiovisual synchrony and asynchrony perception in 6-month-old infants
Abstract
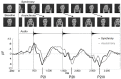
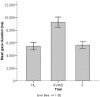
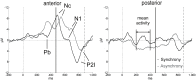
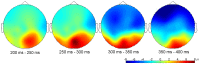
Young infants are sensitive to multisensory temporal synchrony relations, but the neural dynamics of temporal interactions between vision and audition in infancy are not well understood. We investigated audiovisual synchrony and asynchrony perception in 6-month-old infants using event-related brain potentials (ERP). In a prior behavioral experiment (n = 45), infants were habituated to an audiovisual synchronous stimulus and tested for recovery of interest by presenting an asynchronous test stimulus in which the visual stream was delayed with respect to the auditory stream by 400 ms. Infants who behaviorally discriminated the change in temporal alignment were included in further analyses. In the EEG experiment (final sample: n = 15), synchronous and asynchronous stimuli (visual delay of 400 ms) were presented in random order. Results show latency shifts in the auditory ERP components N1 and P2 as well as the infant ERP component Nc. Latencies in the asynchronous condition were significantly longer than in the synchronous condition. After video onset but preceding the auditory onset, amplitude modulations propagating from posterior to anterior sites and related to the Pb component of infants' ERP were observed. Results suggest temporal interactions between the two modalities. Specifically, they point to the significance of anticipatory visual motion for auditory processing, and indicate young infants' predictive capacities for audiovisual temporal synchrony relations.
Keywords: ERP; asynchrony; audiovisual; infancy; multisensory perception; synchrony.
Figures



References
-
- Bahrick L. E. (1983). Infants’ perception of substance and temporal synchrony in multimodal events. Infant Behav. Dev. 6, 429–451 10.1016/S0163-6383(83)90241-2 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

