Rapid phosphatidic acid accumulation in response to low temperature stress in Arabidopsis is generated through diacylglycerol kinase
- PMID: 23346092
- PMCID: PMC3551192
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2013.00001
Rapid phosphatidic acid accumulation in response to low temperature stress in Arabidopsis is generated through diacylglycerol kinase
Abstract
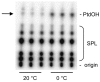
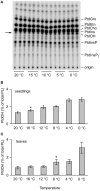
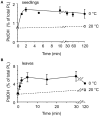
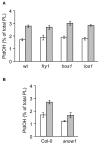
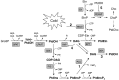
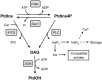
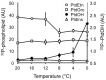
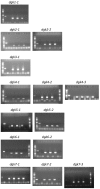
Phosphatidic acid (PtdOH) is emerging as an important signaling lipid in abiotic stress responses in plants. The effect of cold stress was monitored using (32)P-labeled seedlings and leaf discs of Arabidopsis thaliana. Low, non-freezing temperatures were found to trigger a very rapid (32)P-PtdOH increase, peaking within 2 and 5 min, respectively. In principle, PtdOH can be generated through three different pathways, i.e., (1) via de novo phospholipid biosynthesis (through acylation of lyso-PtdOH), (2) via phospholipase D hydrolysis of structural phospholipids, or (3) via phosphorylation of diacylglycerol (DAG) by DAG kinase (DGK). Using a differential (32)P-labeling protocol and a PLD-transphosphatidylation assay, evidence is provided that the rapid (32)P-PtdOH response was primarily generated through DGK. A simultaneous decrease in the levels of (32)P-PtdInsP, correlating in time, temperature dependency, and magnitude with the increase in (32)P-PtdOH, suggested that a PtdInsP-hydrolyzing PLC generated the DAG in this reaction. Testing T-DNA insertion lines available for the seven DGK genes, revealed no clear changes in (32)P-PtdOH responses, suggesting functional redundancy. Similarly, known cold-stress mutants were analyzed to investigate whether the PtdOH response acted downstream of the respective gene products. The hos1, los1, and fry1 mutants were found to exhibit normal PtdOH responses. Slight changes were found for ice1, snow1, and the overexpression line Super-ICE1, however, this was not cold-specific and likely due to pleiotropic effects. A tentative model illustrating direct cold effects on phospholipid metabolism is presented.
Keywords: abiotic stress; cold stress; diacylglycerol kinase; lipid signaling; phosphatidic acid; phosphoinositide; phospholipase; plant signaling.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

