Oncoplastic technique combining an adipofascial flap with an extended glandular flap for the breast-conserving reconstruction of small dense breasts
- PMID: 23346178
- PMCID: PMC3542857
- DOI: 10.4048/jbc.2012.15.4.468
Oncoplastic technique combining an adipofascial flap with an extended glandular flap for the breast-conserving reconstruction of small dense breasts
Abstract
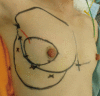
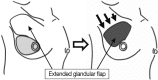
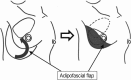
We introduce a method combining two oncoplastic techniques for breast-conserving reconstruction. The procedure is as follows: first, an extended glandular flap is made by undermining the breast from both the skin and the pectoralis fascia to the upper edge of the breast at the subclavicular area. After modeling the breast mound with the extended glandular flap, an inframammary adipofascial flap is made. The flap is reflected back to the breast area remodeled using the extended glandular flap. After reshaping the breast, the inframammary line is then re-shaped. This method is indicated for patients with breast cancer in the outer portion of the breast, who have small dense breasts, and have undergone a large excision of about 40% of their breast volume. We treated four patients, all of whom had either excellent or good cosmetic results with no fat necrosis.
Keywords: Mammaplasty; Segmental mastectomy; Surgical procedures.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Breast-volume displacement using an extended glandular flap for small dense breasts.Plast Surg Int. 2011;2011:359842. doi: 10.1155/2011/359842. Epub 2011 Sep 20. Plast Surg Int. 2011. PMID: 22567239 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term results of breast volume replacement using an inframammary adipofascial flap after breast-conserving surgery.Breast Cancer. 2014 Sep;21(5):635-40. doi: 10.1007/s12282-011-0285-2. Epub 2011 Jun 28. Breast Cancer. 2014. PMID: 21710196
-
A case report of total breast reconstruction using an inframammary adipofascial flap with an implant.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2016;23:109-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2016.04.021. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2016. PMID: 27107500 Free PMC article.
-
Oncoplastic breast surgery combining partial mastectomy with immediate breast reshaping using a keyhole-shaped skin glandular flap for Paget's disease.Surg Today. 2014 Sep;44(9):1783-8. doi: 10.1007/s00595-013-0687-1. Epub 2013 Aug 8. Surg Today. 2014. PMID: 23925716 Review.
-
Oncoplastic breast surgery: comprehensive review.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017 Jun;21(11):2572-2585. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28678328 Review.
Cited by
-
Immediate reconstruction following nipple-sparing mastectomy: one option for young breast cancer patients with early stage disease.J Thorac Dis. 2013 Jun;5(3):200-2. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2013.06.07. J Thorac Dis. 2013. PMID: 23825742 Free PMC article.
-
Oncoplastic Breast Conservation for Central Tumors: Definition, Classification, and the Analysis of Single Institution Experience.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2024 May 6;12(5):e5789. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000005789. eCollection 2024 May. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2024. PMID: 38712017 Free PMC article.
-
Huge myoid hamartoma of the breast treated with reduction mammaplasty: report of a case.Surg Today. 2014 Dec;44(12):2369-73. doi: 10.1007/s00595-014-0833-4. Epub 2014 Jan 28. Surg Today. 2014. PMID: 24468741
References
-
- Bulstrode NW, Shrotria S. Prediction of cosmetic outcome following conservative breast surgery using breast volume measurements. Breast. 2001;10:124–126. - PubMed
-
- Clough KB, Kaufman GJ, Nos C, Buccimazza I, Sarfati IM. Improving breast cancer surgery: a classification and quadrant per quadrant atlas for oncoplastic surgery. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:1375–1391. - PubMed
-
- Ogawa T, Hanamura N, Yamashita M, Ri Y, Kuriyama N, Isaji S. Usefulness of breast-volume replacement using an inframammary adipofascial flap after breast-conservation therapy. Am J Surg. 2007;193:514–518. - PubMed
-
- Ogawa T, Hanamura N, Yamashita M, Kimura H, Kashikura Y. Long-term results of breast volume replacement using an inframammary adipofascial flap after breast-conserving surgery. Breast Cancer. In press. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

