Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of the Ethanolic Extract of Artemisia morrisonensis Hayata in Mice
- PMID: 23346188
- PMCID: PMC3544374
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/138954
Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of the Ethanolic Extract of Artemisia morrisonensis Hayata in Mice
Abstract
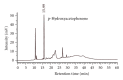
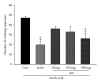
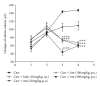
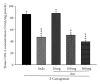
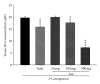
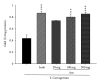
The aim of this study was to investigate the possible analgesic and anti-inflammatory mechanisms of the ethanolic extract of A. morrisonensis Hayata (AM(EtOH)). Two models were employed for evaluation of the analgesic effects: acetic acid-induced writhing response and formalin-induced paw licking. The results demonstrated that AM(EtOH) decreased writhing response for both the acetic acid assay and the licking time in the formalin test. The anti-inflammatory effect was evaluated by paw edema of mice induced by λ-carrageenan. AM(EtOH) significantly decreased induced paw edema three to four hours after λ-carrageenan injection. Additionally, the results indicated that the anti-inflammatory mechanism of AM(EtOH) may be due to the declined levels of nitric oxide (NO) and malondialdehyde (MDA) in the edematous paw. Furthermore, AM(EtOH) decreased the tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels, leading to the reduction of prostaglandins and subsequently alleviated edema. Isolation and purification of the AM(EtOH) extract determined p-hydroxyacetophenone to be a major component at 130 mg/g of extract. No mortality was observed in the acute toxicity test given at the dose of 10 g/kg. This study demonstrated the possible mechanisms for the analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of AM(EtOH) for mice and provided evidence for the ethnobotanical uses of A. morrisonensis in treating inflammatory diseases.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of ethanol root extract of Mahonia oiwakensis in mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2009 Sep 7;125(2):297-303. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2009.06.024. Epub 2009 Jul 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19576980
-
Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of the methanol extract of Elaeagnus oldhamii Maxim. in mice.Am J Chin Med. 2012;40(3):581-97. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X12500449. Am J Chin Med. 2012. PMID: 22745072
-
Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of the methanol extract of Kalanchoe gracilis (L.) DC stem in mice.Am J Chin Med. 2010;38(3):529-46. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X10008032. Am J Chin Med. 2010. PMID: 20503470
-
Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of methanol extract from Desmodium triflorum DC in mice.Am J Chin Med. 2009;37(3):573-88. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X09007065. Am J Chin Med. 2009. PMID: 19606516
-
Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Methanol Extract of Cissus repens in Mice.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:135379. doi: 10.1155/2012/135379. Epub 2012 Sep 6. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012. PMID: 22991570 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Supercritical-Carbon Dioxide Fluid Extract from Flowers and Buds of Chrysanthemum indicum Linnén.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:413237. doi: 10.1155/2013/413237. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 24223056 Free PMC article.
-
Analgesic and Antipyretic Activities of Ethyl Acetate Fraction Tablet of Andrographis paniculata in Animal Models.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Mar 8;2021:8848797. doi: 10.1155/2021/8848797. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 33747115 Free PMC article.
-
p-Hydroxyacetophenone suppresses nuclear factor-κB-related inflammation in nociceptive and inflammatory animal models.J Nat Med. 2017 Apr;71(2):422-432. doi: 10.1007/s11418-017-1074-9. Epub 2017 Feb 1. J Nat Med. 2017. PMID: 28150144
References
-
- Takeuchi T. Revolutionary change in rheumatoid arthritis management with biological therapy. The Keio Journal of Medicine. 2011;60(3):75–81. - PubMed
-
- Majithia V, Geraci SA. Rheumatoid arthritis: diagnosis and management. American Journal of Medicine. 2007;120(11):936–939. - PubMed
-
- Scott DL. Biologics-based therapy for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 2012;91(1):30–43. - PubMed
-
- Murakami A, Ohigashi H. Targeting NOX, INOS and COX-2 in inflammatory cells: chemoprevention using food phytochemicals. International Journal of Cancer. 2007;121(11):2357–2363. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

