A comparison of the performance and application differences between manual and automated patch-clamp techniques
- PMID: 23346269
- PMCID: PMC3549544
- DOI: 10.2174/1875397301206010087
A comparison of the performance and application differences between manual and automated patch-clamp techniques
Abstract
The patch clamp technique is commonly used in electrophysiological experiments and offers direct insight into ion channel properties through the characterization of ion channel activity. This technique can be used to elucidate the interaction between a drug and a specific ion channel at different conformational states to understand the ion channel modulators' mechanisms. The patch clamp technique is regarded as a gold standard for ion channel research; however, it suffers from low throughput and high personnel costs. In the last decade, the development of several automated electrophysiology platforms has greatly increased the screen throughput of whole cell electrophysiological recordings. New advancements in the automated patch clamp systems have aimed to provide high data quality, high content, and high throughput. However, due to the limitations noted above, automated patch clamp systems are not capable of replacing manual patch clamp systems in ion channel research. While automated patch clamp systems are useful for screening large amounts of compounds in cell lines that stably express high levels of ion channels, the manual patch clamp technique is still necessary for studying ion channel properties in some research areas and for specific cell types, including primary cells that have mixed cell types and differentiated cells that derive from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) or embryonic stem cells (ESCs). Therefore, further improvements in flexibility with regard to cell types and data quality will broaden the applications of the automated patch clamp systems in both academia and industry.
Keywords: Automated patch clamp technique; Drug discovery; Drug safety; Induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells; Ion channels; Patch clamp..
Figures
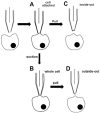
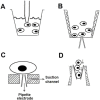
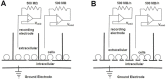
References
-
- Ackerman MJ, Clapham DE. Ion channels--basic science and clinical disease. N Engl J Med. 1997; 336:1575–86. - PubMed
-
- Neher E, Sakmann B. Single-channel currents recorded from membrane of denervated frog muscle fibres. Nature. 1976; 260:799–802. - PubMed
-
- Wang X, Li M. Automated electrophysiology: high throughput of art. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2003; 1:695–708. - PubMed
-
- Dunlop J, Bowlby M, Peri R, Vasilyev D, Arias R. Highthroughput electrophysiology: an emerging paradigm for ionchannel screening and physiology. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008; 7:358–68. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
