Heterologous viral expression systems in fosmid vectors increase the functional analysis potential of metagenomic libraries
- PMID: 23346364
- PMCID: PMC3551230
- DOI: 10.1038/srep01107
Heterologous viral expression systems in fosmid vectors increase the functional analysis potential of metagenomic libraries
Abstract
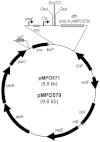
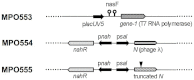
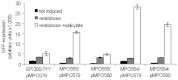
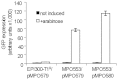
The extraordinary potential of metagenomic functional analyses to identify activities of interest present in uncultured microorganisms has been limited by reduced gene expression in surrogate hosts. We have developed vectors and specialized E. coli strains as improved metagenomic DNA heterologous expression systems, taking advantage of viral components that prevent transcription termination at metagenomic terminators. One of the systems uses the phage T7 RNA-polymerase to drive metagenomic gene expression, while the other approach uses the lambda phage transcription anti-termination protein N to limit transcription termination. A metagenomic library was constructed and functionally screened to identify genes conferring carbenicillin resistance to E. coli. The use of these enhanced expression systems resulted in a 6-fold increase in the frequency of carbenicillin resistant clones. Subcloning and sequence analysis showed that, besides β-lactamases, efflux pumps are not only able contribute to carbenicillin resistance but may in fact be sufficient by themselves to convey carbenicillin resistance.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Escherichia coli strain for thermoinducible T7 RNA polymerase-driven expression.Gene. 1996 Oct 24;177(1-2):267-8. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(96)00294-6. Gene. 1996. PMID: 8921879
-
Design and validation of a transposon that promotes expression of genes in episomal DNA.J Biotechnol. 2020 Feb 20;310:1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2020.01.007. Epub 2020 Jan 16. J Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31954761
-
Engineering efficient termination of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase transcription.G3 (Bethesda). 2022 May 30;12(6):jkac070. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac070. G3 (Bethesda). 2022. PMID: 35348690 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteriophage lambda as a cloning vector.Microbiol Rev. 1992 Dec;56(4):577-91. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.4.577-591.1992. Microbiol Rev. 1992. PMID: 1480110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Regulation of transcription termination in E. coli: antitermination].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 1985 Mar;30(3):197-208. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 1985. PMID: 2988016 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The art of vector engineering: towards the construction of next-generation genetic tools.Microb Biotechnol. 2019 Jan;12(1):125-147. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.13318. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Microb Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30259693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthetic biology approaches to improve biocatalyst identification in metagenomic library screening.Microb Biotechnol. 2015 Jan;8(1):52-64. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.12146. Epub 2014 Aug 13. Microb Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25123225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing Marine Biocatalytic Reservoirs for Green Chemistry Applications through Metagenomic Technologies.Mar Drugs. 2018 Jul 4;16(7):227. doi: 10.3390/md16070227. Mar Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29973493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recovery and functional validation of hidden soil enzymes in metagenomic libraries.Microbiologyopen. 2019 Apr;8(4):e00572. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.572. Epub 2019 Mar 9. Microbiologyopen. 2019. PMID: 30851083 Free PMC article.
-
Members of the uncultured bacterial candidate division WWE1 are implicated in anaerobic digestion of cellulose.Microbiologyopen. 2014 Apr;3(2):157-67. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.144. Epub 2014 Feb 5. Microbiologyopen. 2014. PMID: 24497501 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Uchiyama T. & Miyazaki K. Functional metagenomics for enzyme discovery: challenges to efficient screening. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol 20, 616–622 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Lämmle K. et al. Identification of novel enzymes with different hydrolytic activities by metagenome expression cloning. J Biotechnol 127, 575–592 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

