Chinese urologists' views of practice patterns in the diagnosis and treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia: a nationwide survey
- PMID: 23346486
- PMCID: PMC3547181
- DOI: 10.5213/inj.2012.16.4.191
Chinese urologists' views of practice patterns in the diagnosis and treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia: a nationwide survey
Abstract
Purpose: To assess the compliance of Chinese urologists with China's benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) clinical practice guideline and to explore the diagnosis and therapy modalities for geriatric patients with BPH.
Methods: A cross-sectional survey study was carried out in 33 medical centers in 11 different cities in China. A total of 190 urologists participated in a survey to record their preferences for diagnostic tests and treatment options for BPH outpatients. Diagnostic test results as well as health care demands were collected by surveying 2,027 outpatients aged 60 years and older.
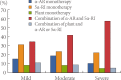
Results: The survey response rate was 97.4%. The respondents generally used the diagnostic tests recommended in China's BPH clinical practice guideline at varying rates. The used rates for medical history, ultrasonography, and urinalysis were above 90.0%; that for uroflowmetry was 31.2%. In addition, the rate of use of recommended tests was higher among doctors in the north than among those in the south. Combination therapy with α-adrenoceptor antagonists and 5α-reductase inhibitors was the preferred treatment option for BPH, and was increasingly used with worsening lower urinary tract symptoms. Finasteride was the most prescribed medication (48.0%), followed by tamsulosin (22.7%).
Conclusions: This study assessed the preferences of urologists in the diagnosis and treatment of BPH, which will serve as an important reference for updating and improving China's current BPH clinical practice guideline.
Keywords: Diagnosis; Practice guideline; Prostatic hyperplasia; Therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Roehrborn CG, McConnell JD. Etiology, pathophysiology, epidemiology and natural history of benign prostatic hyperplasia. In: Walsh PC, Retik AB, Vaughan ED Jr, Wein AJ, Kavoussi LR, Novick AC, et al., editors. Campbell's urology. 8th ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 2002. pp. 1297–1336.
-
- Berry SJ, Coffey DS, Walsh PC, Ewing LL. The development of human benign prostatic hyperplasia with age. J Urol. 1984;132:474–479. - PubMed
-
- Gu FL, Xia TL, Kong XT. Preliminary study of the frequency of benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostatic cancer in China. Urology. 1994;44:688–691. - PubMed
-
- Wei JT, Calhoun E, Jacobsen SJ. Urologic diseases in America project: benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol. 2005;173:1256–1261. - PubMed
-
- McConnell JD, Barry MJ, Bruskewitz RC, Bueschen AJ, Denton SE, Holtgrewe HL, et al. Benign prostatic hyperplasia: diagnosis and treatment (Clinical practice guideline no. 8; AHCPR publication no. 94-0582) Rockville: U.S.: Department of Health and Human Services, Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 1994.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources