Clinical Correlation between Gastric Cancer Type and Serum Selenium and Zinc Levels
- PMID: 23346493
- PMCID: PMC3543971
- DOI: 10.5230/jgc.2012.12.4.217
Clinical Correlation between Gastric Cancer Type and Serum Selenium and Zinc Levels
Abstract
Purpose: We conducted this study to study the clinical correlation between the characteristics of gastric cancer and serum selenium and zinc levels.
Materials and methods: The following data were measured in the baseline serum selenium and zinc levels of 74 patients with curative gastrectomy subsequent to confirmed gastric cancer, from March 2005 to August 2012.
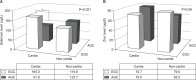
Results: Among the 74 gastric cancer patients, 53 patients were male. Mean serum selenium and zinc levels were 118.7±33.1 ug/L and 72.2±24.3 ug/dl, respectively. Seven patients (9.5%) showed lower selenium level, and 33 patients (44.6%) showed lower zinc level. Serum Selenium level was 99.1±31.8 ug/L in cardia cancer group (10 cases) and 121.8±32.4 ug/L in non-cardia cancer group (64 cases)(P=0.044). According to tumor gross type, zinc level was 78.7±29.6 ug/dl in early gastric cancer (33) and 66.9±17.8 ug/dl in advanced gastric cancer (41) (P=0.064).
Conclusions: The serum selenium level was highly correlated with the location of gastric cancer. The serum zinc level was lower in advanced gastric cancer.
Keywords: Selenium; Stomach neoplasms; Zinc.
Figures
References
-
- Zeng H, Combs GF., Jr Selenium as an anticancer nutrient: roles in cell proliferation and tumor cell invasion. J Nutr Biochem. 2008;19:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Combs GF., Jr Current evidence and research needs to support a health claim for selenium and cancer prevention. J Nutr. 2005;135:343–347. - PubMed
-
- Biesalski HK, Grimm P. Pocket Atlas of Nutrition. 3rd ed. Stuttgart: Georg Thieme Verlag; 2005.
-
- Rotruck JT, Pope AL, Ganther HE, Swanson AB, Hafeman DG, Hoekstra WG. Selenium: biochemical role as a component of glutathione peroxidase. Science. 1973;179:588–590. - PubMed
-
- Rayman MP. The importance of selenium to human health. Lancet. 2000;356:233–241. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources