A case of treatment refractory hyperemesis gravidarum in a patient with comorbid anxiety, treated successfully with adjunctive gabapentin: a review and the potential role of neurogastroentereology in understanding its pathogenesis and treatment
- PMID: 23346516
- PMCID: PMC3552461
A case of treatment refractory hyperemesis gravidarum in a patient with comorbid anxiety, treated successfully with adjunctive gabapentin: a review and the potential role of neurogastroentereology in understanding its pathogenesis and treatment
Abstract
Hyperemesis gravidarum occurs in 0.3 to 10 percent of pregnant women, with a 0.8 percent hospital admission rate. While older theories supported the psychosocial model as a cause for hyperemesis gravidarum, more recent studies have shown significant data to support a biological etiology. Hyperemesis gravidarum has serious complications including include increased risk for miscarriage, low birth weight infants, dehydration, Wernicke's encephalopathy, secondary depression, and negative attitudes toward a consecutive pregnancy. Because of these life-threatening complications and complexity of the disease, it is important to treat both somatic and psychosocial causes of hyperemesis gravidarum to provide the best care for the patient. This paper presents a case of a woman with anxiety symptoms who was experiencing severe nausea and vomiting since Week 2 of pregnancy, with minimal reduction of these symptoms on standard medications utilized in hyperemesis gravidarum. The patient had marked reduction of nausea and vomiting with adjunctive gabapentin. After a brief review of relevant neurogastroenterology, we discuss a possible mechanism for the added gabapentin.
Keywords: Hyperemesis gravidarum; gabapentin; neurogastroenterology.
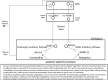
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of gabapentin on hyperemesis gravidarum: a double-blind, randomized controlled trial.Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2021 Jan;3(1):100273. doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2020.100273. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2021. PMID: 33451591 Clinical Trial.
-
Pregnant, miserable, and starving in 21st century America.AJOG Glob Rep. 2022 Dec 5;3(1):100141. doi: 10.1016/j.xagr.2022.100141. eCollection 2023 Feb. AJOG Glob Rep. 2022. PMID: 36536797 Free PMC article.
-
Wernicke's encephalopathy in hyperemesis gravidarum: association with abnormal liver function.Isr J Med Sci. 1994 Mar;30(3):225-8. Isr J Med Sci. 1994. PMID: 8181922 Review.
-
[Wernicke's encephalopathy induced by hyperemesis gravidarum (case report)].Medicina (Kaunas). 2003;39(1):56-61. Medicina (Kaunas). 2003. PMID: 12576766 Lithuanian.
-
Hyperemesis gravidarum: literature review.WMJ. 2003;102(3):46-51. WMJ. 2003. PMID: 12822290 Review.
Cited by
-
Treatment options for hyperemesis gravidarum.Arch Womens Ment Health. 2017 Jun;20(3):363-372. doi: 10.1007/s00737-016-0707-4. Epub 2017 Jan 9. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2017. PMID: 28070660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gabapentin's anti-nausea and anti-emetic effects: a review.Exp Brain Res. 2014 Aug;232(8):2535-9. doi: 10.1007/s00221-014-3905-1. Epub 2014 Mar 26. Exp Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 24668130 Review.
-
Nausea and vomiting of pregnancy - What's new?Auton Neurosci. 2017 Jan;202:62-72. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2016.05.002. Epub 2016 May 13. Auton Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 27209471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Management of Nausea and Vomiting Not Related to Anticancer Therapy in Patients with Cancer.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2021 Jan 14;22(2):17. doi: 10.1007/s11864-020-00813-0. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33443705 Review.
References
-
- Sonkusare S. The clinical management of hyperemesis gravidarum. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2011 Jun;283(6):1183–1192. - PubMed
-
- Ismail SK, Kenny L. Review on hyperemesis gravidarum. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2007;21(5):755–769. - PubMed
-
- Niebyl JR. Clinical practice. Nausea and vomiting in pregnancy. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(16):1544–1550. - PubMed
-
- Koren G, Boskovic R, Hard M, et al. Motherisk-PUQE (pregnancy-unique quantification of emesis and nausea) scoring system for nausea and vomiting of pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2002;186(5 Suppl Understanding):S228–S231. - PubMed
-
- Hamilton M. The Assessment of Anxiety States by Rating. Br J Med Psychol. 1959;32:50–55. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources