Diaryl hydrazones as multifunctional inhibitors of amyloid self-assembly
- PMID: 23346953
- PMCID: PMC3608202
- DOI: 10.1021/bi3012059
Diaryl hydrazones as multifunctional inhibitors of amyloid self-assembly
Abstract
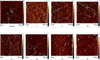
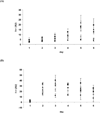
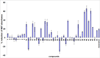
The design and application of an effective, new class of multifunctional small molecule inhibitors of amyloid self-assembly are described. Several compounds based on the diaryl hydrazone scaffold were designed. Forty-four substituted derivatives of this core structure were synthesized using a variety of benzaldehydes and phenylhydrazines and characterized. The inhibitor candidates were evaluated in multiple assays, including the inhibition of amyloid β (Aβ) fibrillogenesis and oligomer formation and the reverse processes, the disassembly of preformed fibrils and oligomers. Because the structure of the hydrazone-based inhibitors mimics the redox features of the antioxidant resveratrol, the radical scavenging effect of the compounds was evaluated by colorimetric assays against 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl and superoxide radicals. The hydrazone scaffold was active in all of the different assays. The structure-activity relationship revealed that the substituents on the aromatic rings had a considerable effect on the overall activity of the compounds. The inhibitors showed strong activity in fibrillogenesis inhibition and disassembly, and even greater potency in the inhibition of oligomer formation and oligomer disassembly. Supporting the quantitative fluorometric and colorimetric assays, size exclusion chromatographic studies indicated that the best compounds practically eliminated or substantially inhibited the formation of soluble, aggregated Aβ species, as well. Atomic force microscopy was also applied to monitor the morphology of Aβ deposits. The compounds also possessed the predicted antioxidant properties; approximately 30% of the synthesized compounds showed a radical scavenging effect equal to or better than that of resveratrol or ascorbic acid.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Organofluorine Hydrazone Derivatives as Multifunctional Anti-Alzheimer's Agents with CK2 Inhibitory and Antioxidant Features.ChemMedChem. 2021 Jun 17;16(12):1927-1932. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202100047. Epub 2021 Apr 8. ChemMedChem. 2021. PMID: 33713036
-
Synthesis, bioactivity and molecular modeling studies on potential anti-Alzheimer piperidinehydrazide-hydrazones.Bioorg Chem. 2019 Jun;87:888-900. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2018.11.051. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Bioorg Chem. 2019. PMID: 30538051
-
Melatonin analogue new indole hydrazide/hydrazone derivatives with antioxidant behavior: synthesis and structure-activity relationships.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2009 Apr;24(2):506-15. doi: 10.1080/14756360802218516. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 18972245
-
Potential antioxidant activity of Morita-Baylis-Hillman adducts.Bioorg Chem. 2018 Aug;78:24-28. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2018.03.004. Epub 2018 Mar 3. Bioorg Chem. 2018. PMID: 29529518 Review.
-
Understanding amyloid fibril nucleation and aβ oligomer/drug interactions from computer simulations.Acc Chem Res. 2014 Feb 18;47(2):603-11. doi: 10.1021/ar4002075. Epub 2013 Dec 24. Acc Chem Res. 2014. PMID: 24368046 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of hydrazone and N-acylhydrazone derivatives of vitamin B6 and pyridine-4-carbaldehyde as potential drugs against Alzheimer's disease.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2024 Dec;39(1):2431832. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2024.2431832. Epub 2024 Dec 9. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39654394 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Features of Small Molecule Antioxidants and Strategic Modifications to Improve Potential Bioactivity.Molecules. 2023 Jan 20;28(3):1057. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031057. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36770724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Solvent- and Catalyst-Free Environmentally Benign High Hydrostatic Pressure-Assisted Synthesis of Bioactive Hydrazones and the Evaluation of Their Stability Under Various Storage Conditions.Molecules. 2024 Nov 8;29(22):5287. doi: 10.3390/molecules29225287. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39598676 Free PMC article.
-
Green synthesis of building blocks, drug candidates and fine chemicals by barochemistry: application of high pressure in organic synthesis.Green Chem. 2025 May 20;27(24):7096-7113. doi: 10.1039/d5gc01075f. eCollection 2025 Jun 16. Green Chem. 2025. PMID: 40452950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis and application of β-carbolines as novel multi-functional anti-Alzheimer's disease agents.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2017 Jan 15;27(2):232-236. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.11.067. Epub 2016 Nov 24. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2017. PMID: 27923619 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wetzel R, editor. Methods in Enzymology. Academic Press; 1999. Amyloid, Prions, and Other Protein Aggregates; p. 309.
-
- Chiti F, Dobson CM. Amyloid formation by globular proteins under native conditions. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008;5:15–22. - PubMed
-
- Walsh DM, Selkoe DJ. Aβ oligomers – a decade of discovery. J. Neurochem. 2007;101:1172–1184. - PubMed
-
- Estrada LD, Soto C. Disrupting beta-amyloid for Alzheimer's disease treatment. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2007;7:115–126. - PubMed
-
- Van der Schyf CJ, Mandel S, Geldenhuys WJ, Amit T, Avramovich Y, Zheng H, Fridkin M, Gal S, Weinreb O, Am OB, Sagi Y, Youdim MBH. Novel multifunctional anti-Alzheimer drugs with various CNS neurotransmitter targets and neuroprotective moieties. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2007;4:522–536. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

