Developmental checkpoints and feedback circuits time insect maturation
- PMID: 23347514
- PMCID: PMC4060521
- DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385979-2.00001-0
Developmental checkpoints and feedback circuits time insect maturation
Abstract
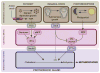
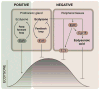
The transition from juvenile to adult is a fundamental process that allows animals to allocate resource toward reproduction after completing a certain amount of growth. In insects, growth to a species-specific target size induces pulses of the steroid hormone ecdysone that triggers metamorphosis and reproductive maturation. The past few years have seen significant progress in understanding the interplay of mechanisms that coordinate timing of ecdysone production and release. These studies show that the neuroendocrine system monitors complex size-related and nutritional signals, as well as external cues, to time production and release of ecdysone. Based on results discussed here, we suggest that developmental progression to adulthood is controlled by checkpoints that regulate the genetic timing program enabling it to adapt to different environmental conditions. These checkpoints utilize a number of signaling pathways to modulate ecdysone production in the prothoracic gland. Release of ecdysone activates an autonomous cascade of both feedforward and feedback signals that determine the duration of the ecdysone pulse at each developmental transitions. Conservation of the genetic mechanisms that coordinate the juvenile-adult transition suggests that insights from the fruit fly Drosophila will provide a framework for future investigation of developmental timing in metazoans.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Ahmed ML, Ong KK, Dunger DB. Childhood obesity and the timing of puberty. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2009;20:237–242. - PubMed
-
- Ainsley JA, Kim MJ, Wegman LJ, Pettus JM, Johnson WA. Sensory mechanisms controlling the timing of larval developmental and behavioral transitions require the Drosophila DEG/ENaC subunit, Pickpocket1. Developmental Biology. 2008;322:46–55. - PubMed
-
- Baehrecke EH. Steroid regulation of programmed cell death during Drosophila development. Cell Death and Differentiation. 2000;7:1057–1062. - PubMed
-
- Beadle G, Tatum E, Glancy C. Food level in relation to rate of development and eye pigmentation in Drosophila melanogaster. The Biological Bulletin. 1938;75:447–462.
-
- Beydon P, Lafont R. Feedback inhibition of ecdysone production by 20-hydroxyecdysone in Pieris brassicae pupae. Journal of Insect Physiology. 1983;29:529–533.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

