Unusual case of severe arrhythmia developed after acute intoxication with tosylchloramide
- PMID: 23347670
- PMCID: PMC3566980
- DOI: 10.1186/2050-6511-14-8
Unusual case of severe arrhythmia developed after acute intoxication with tosylchloramide
Abstract
Background: Drugs not commonly considered to be cardioactive agents may cause prolongation of the QT interval with resultant torsades de pointes and ventricular fibrillation. This form of drug toxicity often causes cardiac arrest or sudden death.
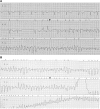
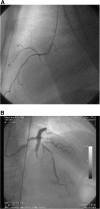
Case presentation: After accidental ingestion of tosylchloramide a caucasian 77-year-old woman, with a family history of cardiovascular disease and hypertension, was admitted to the intensive care unit following episodes of torsades de pointes with a prolonged QT/QTc interval (640/542 ms). The patient received an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator, was discharged from the hospital with normal QT/QTc interval and did not experience additional ventricular arrhythmias during one year of follow-up.
Conclusion: This is the first report concerning an unusual case of torsades de pointes after accidental intoxication by ingestion of tosylchloramide. The pronounced impact of the oxidyzing agent tosylchloramide on the activity of some of the ion channels regulating the QT interval was identified as a probable cause of the arrhythmia.
Figures


Similar articles
-
QTc prolongation and torsades de pointes due to a coadministration of fluoxetine and amiodarone in a patient with implantable cardioverter-defibrillator: Case report and review of the literature.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Dec;96(49):e9071. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009071. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 29245320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
QT Interval prolongation and torsades de pointes due to a coadministration of ciprofloxacin and azimilide in a patient with implantable cardioverter-defibrillator.Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2007 Aug;30(8):1043-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.2007.00809.x. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2007. PMID: 17669094
-
[QT prolongation and torsade de pointes tachycardia during therapy with maprotiline. Differential diagnostic and therapeutic aspects].Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2001 Dec 7;126(49):1396-400. doi: 10.1055/s-2001-18880. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2001. PMID: 11740632 German.
-
[Drug induced QT prolongation].Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2008;120(5-6):128-35. doi: 10.1007/s00508-008-0940-6. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2008. PMID: 18365152 Review. German.
-
A new biomarker--index of cardiac electrophysiological balance (iCEB)--plays an important role in drug-induced cardiac arrhythmias: beyond QT-prolongation and Torsades de Pointes (TdPs).J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2013 Sep-Oct;68(2):250-259. doi: 10.1016/j.vascn.2013.01.003. Epub 2013 Jan 19. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2013. PMID: 23337247
Cited by
-
Pillars and Pitfalls of the New Pharmacovigilance Legislation: Consequences for the Identification of Adverse Drug Reactions Deriving From Abuse, Misuse, Overdose, Occupational Exposure, and Medication Errors.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Jun 12;9:611. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00611. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29946258 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between a Prolonged Corrected QT Interval and Mortality in Patients Presenting with Syncope at the Emergency Department.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Nov 24;2021:5441670. doi: 10.1155/2021/5441670. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34869765 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blasco A, Joral A, Fuente R, Rodríguez M, García A, Domínguez A. Bronchial asthma due to sensitization to chloramine T. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 1992;2:167–170. - PubMed
-
- Grant WM. Toxicology of the eye. Charles C. Thomas, Srpingfield; 1974.
-
- Pascuzzi TA, Storrow AB. Mass casualties from acute inhalation of chloramine gas. Mil Med. 1998;163:102–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

