Increase of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition with celecoxib combined with 5-FU enhances tumor cell apoptosis and antitumor efficacy in a subcutaneous implantation tumor model of human colon cancer
- PMID: 23347845
- PMCID: PMC3599060
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7819-11-16
Increase of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition with celecoxib combined with 5-FU enhances tumor cell apoptosis and antitumor efficacy in a subcutaneous implantation tumor model of human colon cancer
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study was to investigate the anti-tumor effect and explore the mechanisms of celecoxib (a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor) combined with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) on the treatment of human colorectal cancer in a BALB/C nude mouse subcutaneous xenograft model.
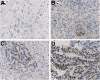
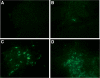
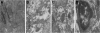
Methods: Effects of celecoxib combined with 5-FU on the proliferation of xenograft carcinoma induced by HT-29 were investigated. The apoptotic cells were detected by electron microscope and TUNEL (terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling) assay. Immunohistochemistry and Western blot were used to estimate the expression of cytochrome C, caspase-3 and caspase-9.
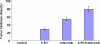
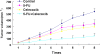
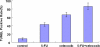
Results: Compared with the control group, treatment groups showed significant inhibition of tumor growth. More apoptotic cells existed after treatment with celecoxib combined with 5-FU. Cytochrome C, caspase-3 and caspase-9 were increased in treated groups, and more obviously in the drug combination group. Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) were decreased after treatment with celecoxib only or combined with 5-FU. And the combined group showed a greater decrease.
Conclusions: Celecoxib combined with 5-FU could inhibit the growth of tumors in vivo by inducing apoptosis and activation of the cytochrome C dependency apoptosis signal pathway. A decrease of COX-2 and an increase of cytochrome C, caspase-3 and caspase-9 may be involved in this process.
Figures


References
-
- Debatin K. Activation of apoptosis pathways by anticancer treatment. Toxicol Lett. 2000;112:41–48. - PubMed
-
- Cassidy J, Saltz L, Twelves C, Van Cutsem E, Hoff P, Kang Y, Saini JP, Gilberg F, Cunningham D. Efficacy of capecitabine versus 5-fluorouracil in colorectal and gastric cancers: a meta-analysis of individual data from 6171 patients. Ann Oncol. 2011;22:2604–2609. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdr031. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kodama Y, Fumoto S, Nishi J, Nakashima M, Sasaki H, Nakamura J, Nishida K. Absorption and distribution characteristics of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) after an application to the liver surface in rats in order to reduce systemic side effects. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008;31:1049–1052. doi: 10.1248/bpb.31.1049. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

