The biosynthesis of nitrogen-, sulfur-, and high-carbon chain-containing sugars
- PMID: 23348524
- PMCID: PMC3641179
- DOI: 10.1039/c2cs35438a
The biosynthesis of nitrogen-, sulfur-, and high-carbon chain-containing sugars
Abstract
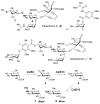
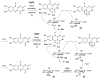
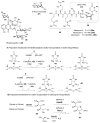
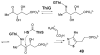
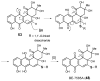
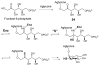
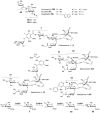
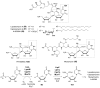
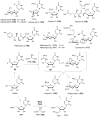
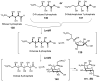
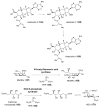
Carbohydrates serve many structural and functional roles in biology. While the majority of monosaccharides are characterized by the chemical composition (CH2O)n, modifications including deoxygenation, C-alkylation, amination, O- and N-methylation, which are characteristic of many sugar appendages of secondary metabolites, are not uncommon. Interestingly, some sugar molecules are formed via modifications including amine oxidation, sulfur incorporation, and "high-carbon" chain attachment. Most of these unusual sugars have been identified over the past several decades as components of microbially produced natural products, although a few high-carbon sugars are also found in the lipooligosaccharides of the outer cell walls of Gram-negative bacteria. Despite their broad distribution in nature, these sugars are considered "rare" due to their relative scarcity. The biosynthetic steps that underlie their formation continue to perplex researchers to this day and many questions regarding key transformations remain unanswered. This review will focus on our current understanding of the biosynthesis of unusual sugars bearing oxidized amine substituents, thio-functional groups, and high-carbon chains.
Figures












Similar articles
-
Increasing carbohydrate diversity via amine oxidation: aminosugar, hydroxyaminosugar, nitrososugar, and nitrosugar biosynthesis in bacteria.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2008 Jun;12(3):297-305. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2008.03.017. Epub 2008 Apr 18. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2008. PMID: 18424273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unusual sugar biosynthesis and natural product glycodiversification.Nature. 2007 Apr 26;446(7139):1008-16. doi: 10.1038/nature05814. Nature. 2007. PMID: 17460661 Review.
-
Planning Implications Related to Sterilization-Sensitive Science Investigations Associated with Mars Sample Return (MSR).Astrobiology. 2022 Jun;22(S1):S112-S164. doi: 10.1089/AST.2021.0113. Epub 2022 May 19. Astrobiology. 2022. PMID: 34904892
-
Natural Products Containing a Nitrogen-Sulfur Bond.J Nat Prod. 2018 Feb 23;81(2):423-446. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.7b00921. Epub 2018 Jan 24. J Nat Prod. 2018. PMID: 29364663
-
Natural-product sugar biosynthesis and enzymatic glycodiversification.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2008;47(51):9814-59. doi: 10.1002/anie.200801204. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2008. PMID: 19058170 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural characterization of AtmS13, a putative sugar aminotransferase involved in indolocarbazole AT2433 aminopentose biosynthesis.Proteins. 2015 Aug;83(8):1547-54. doi: 10.1002/prot.24844. Epub 2015 Jul 1. Proteins. 2015. PMID: 26061967 Free PMC article.
-
Neoglycosylation and neoglycorandomization: Enabling tools for the discovery of novel glycosylated bioactive probes and early stage leads.Medchemcomm. 2014 Aug 1;5(8):1036-1047. doi: 10.1039/C4MD00117F. Medchemcomm. 2014. PMID: 25071927 Free PMC article.
-
An atypical orphan carbohydrate-NRPS genomic island encodes a novel lytic transglycosylase.Chem Biol. 2014 Oct 23;21(10):1271-1277. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2014.07.025. Epub 2014 Sep 11. Chem Biol. 2014. PMID: 25219963 Free PMC article.
-
C-S bond cleavage by a polyketide synthase domain.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Aug 18;112(33):10359-64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1508437112. Epub 2015 Aug 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26240335 Free PMC article.
-
Use of a Tyrosine Analogue To Modulate the Two Activities of a Nonheme Iron Enzyme OvoA in Ovothiol Biosynthesis, Cysteine Oxidation versus Oxidative C-S Bond Formation.J Am Chem Soc. 2018 Apr 4;140(13):4604-4612. doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b13628. Epub 2018 Mar 21. J Am Chem Soc. 2018. PMID: 29544051 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

