Mapping kainate activation of inner neurons in the rat retina
- PMID: 23348566
- PMCID: PMC4048659
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.23305
Mapping kainate activation of inner neurons in the rat retina
Abstract
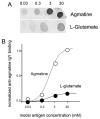
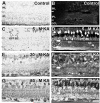
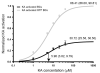
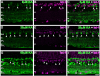
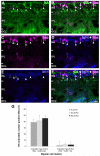
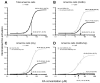
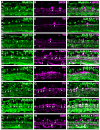
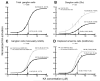
Kainate receptors mediate fast, excitatory synaptic transmission for a range of inner neurons in the mammalian retina. However, allocation of functional kainate receptors to known cell types and their sensitivity remains unresolved. Using the cation channel probe 1-amino-4-guanidobutane agmatine (AGB), we investigated kainate sensitivity of neurochemically identified cell populations within the structurally intact rat retina. Most inner retinal neuron populations responded to kainate in a concentration-dependent manner. OFF cone bipolar cells demonstrated the highest sensitivity of all inner neurons to kainate. Immunocytochemical localization of AGB and macromolecular markers confirmed that type 2 bipolar cells were part of this kainate-sensitive population. The majority of amacrine (ACs) and ganglion cells (GCs) showed kainate responses with different sensitivities between major neurochemical classes (γ-aminobutyric acid [GABA]/glycine ACs > glycine ACs > GABA ACs; glutamate [Glu]/weakly GABA GCs > Glu GCs). Conventional and displaced cholinergic ACs were highly responsive to kainate, whereas dopaminergic ACs do not appear to express functional kainate receptors. These findings further contribute to our understanding of neuronal networks in complex multicellular tissues.
Copyright © 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
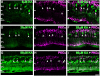
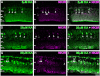
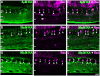
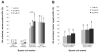
Similar articles
-
Inner retinal neurons display differential responses to N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor activation.J Comp Neurol. 2003 Oct 6;465(1):38-56. doi: 10.1002/cne.10830. J Comp Neurol. 2003. PMID: 12926015
-
Kainate activation of horizontal, bipolar, amacrine, and ganglion cells in the rabbit retina.J Comp Neurol. 1999 Apr 28;407(1):65-76. J Comp Neurol. 1999. PMID: 10213188
-
Mapping glutamatergic drive in the vertebrate retina with a channel-permeant organic cation.J Comp Neurol. 1999 Apr 28;407(1):47-64. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9861(19990428)407:1<47::aid-cne4>3.0.co;2-0. J Comp Neurol. 1999. PMID: 10213187
-
[The post-synaptic glycine receptor mediates in a transitory and sustained way the glycinergic inhibition in the vertebrate retina].Rev Neurol. 2012 Jul 1;55(1):38-46. Rev Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22718408 Review. Spanish.
-
Synaptology of the inner plexiform layer in the anuran retina.Microsc Res Tech. 2000 Sep 1;50(5):394-402. doi: 10.1002/1097-0029(20000901)50:5<394::AID-JEMT8>3.0.CO;2-Q. Microsc Res Tech. 2000. PMID: 10941175 Review.
Cited by
-
Müller Cell Metabolic Signatures: Evolutionary Conservation and Disruption in Disease.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Apr;31(4):320-329. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2020.01.005. Epub 2020 Feb 24. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32187524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression and distribution of peroxiredoxins in the retina and optic nerve.Brain Struct Funct. 2016 Nov;221(8):3903-3925. doi: 10.1007/s00429-015-1135-3. Epub 2015 Oct 26. Brain Struct Funct. 2016. PMID: 26501408 Free PMC article.
-
Visual Disfunction due to the Selective Effect of Glutamate Agonists on Retinal Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 10;22(12):6245. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126245. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34200611 Free PMC article.
-
Functional architecture of the retina: development and disease.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2014 Sep;42:44-84. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2014.06.003. Epub 2014 Jun 28. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2014. PMID: 24984227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of Müller cell glutamine synthetase immunoreactivity is associated with neuronal changes in late-stage retinal degeneration.Front Neuroanat. 2023 Mar 7;17:997722. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2023.997722. eCollection 2023. Front Neuroanat. 2023. PMID: 36960036 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acosta ML, Chua J, Kalloniatis M. Functional activation of glutamate ionotropic receptors in the developing mouse retina. J Comp Neurol. 2007;500:923–941. - PubMed
-
- Andrade da Costa BL, de Mello FG, Hokoc JN. Comparative study of glutamate mediated gamma-aminobutyric acid release from nitric oxide synthase and tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactive cells of the Cebus apella retina. Neurosci Lett. 2001;302:21–24. - PubMed
-
- Brandstätter JH, Hartveit E, Sassoe-Pognetto M, Wässle H. Expression of NMDA and high-affinity kainate receptor subunit mRNAs in the adult rat retina. Eur J Neurosci. 1994;6:1100–1112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

