Ubiquitylation and the pathogenesis of hypertension
- PMID: 23348731
- PMCID: PMC3561829
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI66882
Ubiquitylation and the pathogenesis of hypertension
Abstract
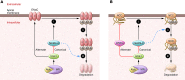
Liddle syndrome is monogenic hypertension caused by mutations in the epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) that interfere with its ubiquitylation by Nedd4-2. In this issue, Ronzaud and colleagues found that deleting Nedd4-2 from kidney tubules in adult mice led to ENaC accumulation, but not at the plasma membrane, as predicted from current models. Instead, abundance of the sodium chloride transporter NCC increased at the plasma membrane, and the mice have some features of increased NCC activity. Together, the results suggest that defective ubiquitylation of ENaC by Nedd4-2 may not fully explain Liddle syndrome and that Nedd4-2 modulates NCC more strongly.
Figures
Comment on
-
Renal tubular NEDD4-2 deficiency causes NCC-mediated salt-dependent hypertension.J Clin Invest. 2013 Feb;123(2):657-65. doi: 10.1172/JCI61110. Epub 2013 Jan 25. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 23348737 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

