Renal tubular NEDD4-2 deficiency causes NCC-mediated salt-dependent hypertension
- PMID: 23348737
- PMCID: PMC3561795
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI61110
Renal tubular NEDD4-2 deficiency causes NCC-mediated salt-dependent hypertension
Abstract
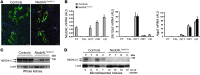
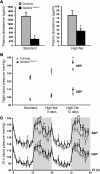
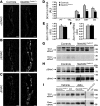
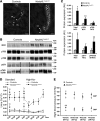
The E3 ubiquitin ligase NEDD4-2 (encoded by the Nedd4L gene) regulates the amiloride-sensitive epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC/SCNN1) to mediate Na+ homeostasis. Mutations in the human β/γENaC subunits that block NEDD4-2 binding or constitutive ablation of exons 6-8 of Nedd4L in mice both result in salt-sensitive hypertension and elevated ENaC activity (Liddle syndrome). To determine the role of renal tubular NEDD4-2 in adult mice, we generated tetracycline-inducible, nephron-specific Nedd4L KO mice. Under standard and high-Na+ diets, conditional KO mice displayed decreased plasma aldosterone but normal Na+/K+ balance. Under a high-Na+ diet, KO mice exhibited hypercalciuria and increased blood pressure, which were reversed by thiazide treatment. Protein expression of βENaC, γENaC, the renal outer medullary K+ channel (ROMK), and total and phosphorylated thiazide-sensitive Na+Cl- cotransporter (NCC) levels were increased in KO kidneys. Unexpectedly, Scnn1a mRNA, which encodes the αENaC subunit, was reduced and proteolytic cleavage of αENaC decreased. Taken together, these results demonstrate that loss of NEDD4-2 in adult renal tubules causes a new form of mild, salt-sensitive hypertension without hyperkalemia that is characterized by upregulation of NCC, elevation of β/γENaC, but not αENaC, and a normal Na+/K+ balance maintained by downregulation of ENaC activity and upregulation of ROMK.
Figures
Comment in
-
Ubiquitylation and the pathogenesis of hypertension.J Clin Invest. 2013 Feb;123(2):546-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI66882. Epub 2013 Jan 25. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 23348731 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

