Platelet ITAM signaling is critical for vascular integrity in inflammation
- PMID: 23348738
- PMCID: PMC3561801
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI65154
Platelet ITAM signaling is critical for vascular integrity in inflammation
Abstract
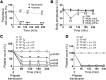
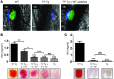
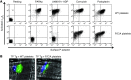
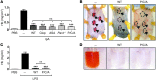
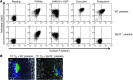
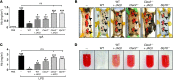
Platelets play a critical role in maintaining vascular integrity during inflammation, but little is known about the underlying molecular mechanisms. Here we report that platelet immunoreceptor tyrosine activation motif (ITAM) signaling, but not GPCR signaling, is critical for the prevention of inflammation-induced hemorrhage. To generate mice with partial or complete defects in these signaling pathways, we developed a protocol for adoptive transfer of genetically and/or chemically inhibited platelets into thrombocytopenic (TP) mice. Unexpectedly, platelets with impaired GPCR signaling, a crucial component of platelet plug formation and hemostasis, were indistinguishable from WT platelets in their ability to prevent hemorrhage at sites of inflammation. In contrast, inhibition of GPVI or genetic deletion of Clec2, the only ITAM receptors expressed on mouse platelets, significantly reduced the ability of platelets to prevent inflammation-induced hemorrhage. Moreover, transfusion of platelets without ITAM receptor function or platelets lacking the adapter protein SLP-76 into TP mice had no significant effect on vascular integrity during inflammation. These results indicate that the control of vascular integrity is a major function of immune-type receptors in platelets, highlighting a potential clinical complication of novel antithrombotic agents directed toward the ITAM signaling pathway.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL050545/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL094594/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016086/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007149/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL106009/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL103432/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL006350/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HL099175/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL006350/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL072798/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL067311/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL072798/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL106009/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL50545/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

