A systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between depression and insulin resistance
- PMID: 23349152
- PMCID: PMC3554272
- DOI: 10.2337/dc12-1442
A systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between depression and insulin resistance
Erratum in
- Diabetes Care. 2013 May;36(5):1429
Abstract
Objective: Depression is associated with the onset of type 2 diabetes. A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies, controlled trials, and unpublished data was conducted to examine the association between depression and insulin resistance (IR).
Research design and methods: Medline, EMBASE, and PsycINFO were searched for studies published up to September 2011. Two independent reviewers assessed the eligibility of each report based on predefined inclusion criteria (study design and measure of depression and IR, excluding prevalent cases of diabetes). Individual effect sizes were standardized, and a meta-analysis was performed to calculate a pooled effect size using random effects. Subgroup analyses and meta-regression were conducted to explore any potential source of heterogeneity between studies.
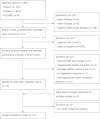
Results: Of 967 abstracts reviewed, 21 studies met the inclusion criteria of which 18 studies had appropriate data for the meta-analysis (n = 25,847). The pooled effect size (95% CI) was 0.19 (0.11-0.27) with marked heterogeneity (I(2) = 82.2%) using the random-effects model. Heterogeneity between studies was not explained by age or sex, but could be partly explained by the methods of depression and IR assessments.
Conclusions: A small but significant cross-sectional association was observed between depression and IR, despite heterogeneity between studies. The pathophysiology mechanisms and direction of this association need further study using a purposively designed prospective or intervention study in samples at high risk for diabetes.
Figures


Comment in
-
Comment on: Kan et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between depression and insulin resistance. Diabetes Care 2013;36:480-489.Diabetes Care. 2013 Aug;36(8):e123. doi: 10.2337/dc13-0403. Diabetes Care. 2013. PMID: 23881976 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Response to Comment on: Kan et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between depression and insulin resistance. Diabetes Care 2013;36:480-489.Diabetes Care. 2013 Aug;36(8):e124. doi: 10.2337/dc13-0729. Diabetes Care. 2013. PMID: 23881977 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Anderson RJ, Freedland KE, Clouse RE, Lustman PJ. The prevalence of comorbid depression in adults with diabetes: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2001;24:1069–1078 - PubMed
-
- Lustman PJ, Clouse RE. Depression in diabetic patients: the relationship between mood and glycemic control. J Diabetes Complications 2005;19:113–122 - PubMed
-
- de Groot M, Anderson R, Freedland KE, Clouse RE, Lustman PJ. Association of depression and diabetes complications: a meta-analysis. Psychosom Med 2001;63:619–630 - PubMed
-
- Ismail K, Winkley K, Stahl D, Chalder T, Edmonds M. A cohort study of people with diabetes and their first foot ulcer: the role of depression on mortality. Diabetes Care 2007;30:1473–1479 - PubMed
-
- Katon WJ, Rutter C, Simon G, et al. The association of comorbid depression with mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2005;28:2668–2672 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

