The clinical characteristics, therapy and outcome of 85 adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and t(4;11)(q21;q23)/MLL-AFF1 prospectively treated in the UKALLXII/ECOG2993 trial
- PMID: 23349309
- PMCID: PMC3669452
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2012.081877
The clinical characteristics, therapy and outcome of 85 adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and t(4;11)(q21;q23)/MLL-AFF1 prospectively treated in the UKALLXII/ECOG2993 trial
Abstract
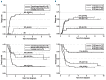
The biology and outcome of adult t(4;11)(q21;q23)/MLL-AFF1 acute lymphoblastic leukemia are poorly understood. We describe the outcome and delineate prognostic factors and optimal post-remission therapy in 85 consecutive patients (median age 38 years) treated uniformly in the prospective trial UKALLXII/ECOG2993. The immunophenotype of this leukemia was pro-B (CD10(NEG)). Immaturity was further suggested by high expression of the stem-cell antigens, CD133 and CD135, although CD34 expression was significantly lower than in t(4;11)-negative patients. Complete remission was achieved in 77 (93%) patients but only 35% survived 5 years (95% CI: 25-45%); the relapse rate was 45% (95% CI: 33-58%). Thirty-one patients underwent allogeneic transplantation in first remission (15 sibling donors and 16 unrelated donors): with 5-year survival rates of 56% and 67% respectively, only 2/31 patients relapsed. This compares with a 24% survival rate and 59% relapse rate in 46 patients who received post-remission chemotherapy. A major determinant of outcome was age with 71% of patients aged <25 years surviving. Younger patients had lower relapse rates (19%) but most received allografts in first complete remission. In conclusion, multivariate analysis did not demonstrate an advantage of allografting over chemotherapy but only five younger patients received chemotherapy. Prospective trials are required to determine whether poor outcomes in older patients can be improved by reduced-intensity conditioning allografts. NCT00002514 www.clinicaltrials.gov.
Figures


References
-
- Goldstone AH, Richards SM, Lazarus HM, Tallman MS, Buck G, Fielding AK, et al. In adults with standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia, the greatest benefit is achieved from a matched sibling allogeneic transplantation in first complete remission, and an autologous transplantation is less effective than conventional consolidation/maintenance chemotherapy in all patients: final results of the International ALL Trial (MRC UKALL XII/ECOG E2993). Blood. 2008;111 (4):1827–33 - PubMed
-
- Rowe JM, Buck G, Burnett AK, Chopra R, Wiernik PH, Richards SM, et al. Induction therapy for adults with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: results of more than 1500 patients from the international ALL trial: MRC UKALL XII/ECOG 2993. Blood. 2005;106(12):3760–7 - PubMed
-
- Moorman AV, Harrison CJ, Buck GA, Richards SM, Secker-Walker LM, Martineau M, et al. Karyotype is an independent prognostic factor in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: analysis of cytogenetic data from patients treated on the MRC UKALL XII/ECOG 2993 trial. Blood. 2007;109(8): 3189–97 - PubMed
-
- Moorman AV. The clinical relevance of chromosomal and genomic abnormalities in B cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Blood Rev. 2012;26(3):123–35 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U10 CA013650/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA021115/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA13650/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA017145/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA066636/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA14958/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA14548/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA014958/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA66636/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037403/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA17145/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA014548/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA023318/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA21115/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA114737/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA23318/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA14588/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- G8223452/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

