Inactivation or loss of TTP promotes invasion in head and neck cancer via transcript stabilization and secretion of MMP9, MMP2, and IL-6
- PMID: 23349315
- PMCID: PMC3594656
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-2927
Inactivation or loss of TTP promotes invasion in head and neck cancer via transcript stabilization and secretion of MMP9, MMP2, and IL-6
Abstract
Purpose: Invasion is the critical step in progression of a precancerous lesion to squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (HNSCC). Invasion is regulated by multiple proinflammatory mediators. Tristetraprolin (TTP) is an mRNA-degrading protein that regulates multiple proinflammatory mediators. TTP may serve as an excellent treatment target. Rap1 is a ras-like oncoprotein that induces critical signaling pathways. In this study, the role of rap1 in TTP-mediated invasion was investigated.
Experimental design: Using complementary approaches, we modulated TTP and altered expression of interleukin (IL)-6 and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 2/9, which were quantified by ELISA and zymogram. Invasion was evaluated in vitro using the oral-cancer-equivalent (OCE) three-dimensional model and in vivo in the chick chorioallantoic membrane (CAM). The role of rap1 and p38 were established using knockdown strategies.
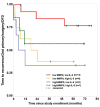
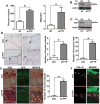
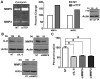
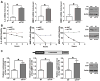
Results: Downregulation of TTP significantly increased invasion via secretion of MMP9/2 and IL-6. In the novel OCE and CAM invasion models of HNSCC, cells with downregulated TTP destroyed the basement membrane to invade the underlying connective tissue. Rap1 induces p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38)-mediated inactivation of TTP. Inactive TTP enhances transcript stability via binding to the 3'-untranslated region (UTR). High IL-6 and MMP9 are prognostic for poor clinical outcomes in patients with HNSCC.
Conclusions: Targeting the rap1-p38-TTP cascade is an attractive novel treatment strategy in HNSCC to concurrently suppress multiple mediators of invasion.
©2012 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tristetraprolin regulates interleukin-6, which is correlated with tumor progression in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer. 2011 Jun 15;117(12):2677-89. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25859. Epub 2011 Jan 10. Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21656745 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblasts and extracellular matrix differently modulate MMP activation by primary and metastatic head and neck cancer cells.Med Oncol. 2012 Jun;29(2):690-703. doi: 10.1007/s12032-011-9871-6. Epub 2011 Mar 6. Med Oncol. 2012. PMID: 21380786
-
Tristetraprolin regulates interleukin-6 expression through p38 MAPK-dependent affinity changes with mRNA 3' untranslated region.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011 Aug;31(8):629-37. doi: 10.1089/jir.2010.0154. Epub 2011 Apr 3. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011. PMID: 21457063 Free PMC article.
-
TTP mediates cisplatin-induced apoptosis of head and neck cancer cells by down-regulating the expression of Bcl-2.J Chemother. 2015 Jun;27(3):174-80. doi: 10.1179/1973947814Y.0000000234. Epub 2015 Jan 21. J Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25604244
-
Characterization of squamous cell carcinoma in an organotypic culture via subsurface non-linear optical molecular imaging.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2013 Nov 1;238(11):1233-41. doi: 10.1177/1535370213502628. Epub 2013 Oct 1. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2013. PMID: 24085785 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Roles of Tristetraprolin in Tumorigenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 29;19(11):3384. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113384. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30380668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-transcriptional regulation of MMP2 mRNA by its interaction with miR-20a and Nucleolin in breast cancer cell lines.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Mar;48(3):2315-2324. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06261-9. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33788053
-
The Histone Methyltransferase EZH2 Mediates Tumor Progression on the Chick Chorioallantoic Membrane Assay, a Novel Model of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Transl Oncol. 2013 Jun 1;6(3):273-81. doi: 10.1593/tlo.13175. Print 2013 Jun. Transl Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23730406 Free PMC article.
-
GASP1 enhances malignant phenotypes of breast cancer cells and decreases their response to paclitaxel by forming a vicious cycle with IGF1/IGF1R signaling pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Aug 30;13(8):751. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05198-6. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36042202 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin shows anti-tumor effect in hepatocellular carcinoma LM3 cells by abrogating JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway.Cancer Med. 2019 Aug;8(10):4806-4820. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2388. Epub 2019 Jul 5. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 31273958 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leemans CR, Braakhuis BJ, Brakenhoff RH. The molecular biology of head and neck cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:9–22. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300. - PubMed
-
- Badache A, Hynes NE. Interleukin 6 inhibits proliferation and, in cooperation with an epidermal growth factor receptor autocrine loop, increases migration of T47D breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2001;61:383–91. - PubMed
-
- Kanazawa T, Nishino H, Hasegawa M, Ohta Y, Iino Y, Ichimura K, et al. Interleukin-6 directly influences proliferation and invasion potential of head and neck cancer cells. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2007;264:815–21. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

