SIVagm infection in wild African green monkeys from South Africa: epidemiology, natural history, and evolutionary considerations
- PMID: 23349627
- PMCID: PMC3547836
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003011
SIVagm infection in wild African green monkeys from South Africa: epidemiology, natural history, and evolutionary considerations
Abstract
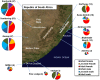
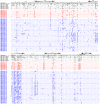
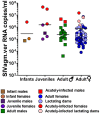
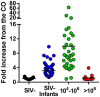
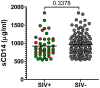
Pathogenesis studies of SIV infection have not been performed to date in wild monkeys due to difficulty in collecting and storing samples on site and the lack of analytical reagents covering the extensive SIV diversity. We performed a large scale study of molecular epidemiology and natural history of SIVagm infection in 225 free-ranging AGMs from multiple locations in South Africa. SIV prevalence (established by sequencing pol, env, and gag) varied dramatically between infant/juvenile (7%) and adult animals (68%) (p<0.0001), and between adult females (78%) and males (57%). Phylogenetic analyses revealed an extensive genetic diversity, including frequent recombination events. Some AGMs harbored epidemiologically linked viruses. Viruses infecting AGMs in the Free State, which are separated from those on the coastal side by the Drakensberg Mountains, formed a separate cluster in the phylogenetic trees; this observation supports a long standing presence of SIV in AGMs, at least from the time of their speciation to their Plio-Pleistocene migration. Specific primers/probes were synthesized based on the pol sequence data and viral loads (VLs) were quantified. VLs were of 10(4)-10(6) RNA copies/ml, in the range of those observed in experimentally-infected monkeys, validating the experimental approaches in natural hosts. VLs were significantly higher (10(7)-10(8) RNA copies/ml) in 10 AGMs diagnosed as acutely infected based on SIV seronegativity (Fiebig II), which suggests a very active transmission of SIVagm in the wild. Neither cytokine levels (as biomarkers of immune activation) nor sCD14 levels (a biomarker of microbial translocation) were different between SIV-infected and SIV-uninfected monkeys. This complex algorithm combining sequencing and phylogeny, VL quantification, serology, and testing of surrogate markers of microbial translocation and immune activation permits a systematic investigation of the epidemiology, viral diversity and natural history of SIV infection in wild African natural hosts.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Factors associated with siman immunodeficiency virus transmission in a natural African nonhuman primate host in the wild.J Virol. 2014 May;88(10):5687-705. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03606-13. Epub 2014 Mar 12. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24623416 Free PMC article.
-
Simian immunodeficiency virus SIVagm.sab infection of Caribbean African green monkeys: a new model for the study of SIV pathogenesis in natural hosts.J Virol. 2006 May;80(10):4858-67. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.10.4858-4867.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16641277 Free PMC article.
-
Mosaic genome structure of simian immunodeficiency virus from west African green monkeys.EMBO J. 1994 Jun 15;13(12):2935-47. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06588.x. EMBO J. 1994. PMID: 8026477 Free PMC article.
-
The history of SIVS and AIDS: epidemiology, phylogeny and biology of isolates from naturally SIV infected non-human primates (NHP) in Africa.Front Biosci. 2004 Jan 1;9:225-54. doi: 10.2741/1154. Front Biosci. 2004. PMID: 14766362 Review.
-
SIVagm: genetic and biological features associated with replication.Front Biosci. 2003 Sep 1;8:d1170-85. doi: 10.2741/1130. Front Biosci. 2003. PMID: 12957815 Review.
Cited by
-
Local Virus Extinctions following a Host Population Bottleneck.J Virol. 2015 Aug;89(16):8152-61. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00671-15. Epub 2015 May 27. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26018153 Free PMC article.
-
CCR5 as a Coreceptor for Human Immunodeficiency Virus and Simian Immunodeficiency Viruses: A Prototypic Love-Hate Affair.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 27;13:835994. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.835994. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35154162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MHC polymorphism in Caribbean African green monkeys.Immunogenetics. 2014 Jun;66(6):353-60. doi: 10.1007/s00251-014-0770-9. Epub 2014 Mar 28. Immunogenetics. 2014. PMID: 24676686
-
Baboon CD8 T cells suppress SIVmac infection in CD4 T cells through contact-dependent production of MIP-1α, MIP-1β, and RANTES.Cytokine. 2018 Nov;111:408-419. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.05.022. Epub 2018 May 26. Cytokine. 2018. PMID: 29807688 Free PMC article.
-
Zoonotic Potential of Simian Arteriviruses.J Virol. 2015 Nov 11;90(2):630-5. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01433-15. Print 2016 Jan 15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26559828 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Worobey M, Telfer P, Souquière S, Hunter M, Coleman CA, et al. (2010) Island biogeography reveals the deep history of SIV. Science 330: 1487. - PubMed
-
- Groves C (2001) Primate taxonomy. Washington, DC: Smithsonian Institution Press.
-
- Groves CP (2005) Order Primates. In: Wilson DE, Reeder DM, editors. Mammal Species of the World. Baltimore, MD: The Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 111–184.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

