Transcription of a cis-acting, noncoding, small RNA is required for pilin antigenic variation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- PMID: 23349628
- PMCID: PMC3547852
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003074
Transcription of a cis-acting, noncoding, small RNA is required for pilin antigenic variation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Abstract
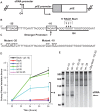
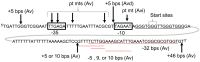
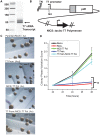
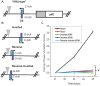
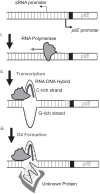
The strict human pathogen Neisseria gonorrhoeae can utilize homologous recombination to generate antigenic variability in targets of immune surveillance. To evade the host immune response, N. gonorrhoeae promotes high frequency gene conversion events between many silent pilin copies and the expressed pilin locus (pilE), resulting in the production of variant pilin proteins. Previously, we identified a guanine quartet (G4) structure localized near pilE that is required for the homologous recombination reactions leading to pilin antigenic variation (Av). In this work, we demonstrate that inactivating the promoter of a small non-coding RNA (sRNA) that initiates within the G4 forming sequence blocks pilin Av. The sRNA promoter is conserved in all sequenced gonococcal strains, and mutations in the predicted transcript downstream of the G4 forming sequence do not alter pilin Av. A mutation that produces a stronger promoter or substitution of the pilE G4-associated sRNA promoter with a phage promoter (when the phage polymerase was expressed) produced wild-type levels of pilin Av. Altering the direction and orientation of the pilE G4-associated sRNA disrupted pilin Av. In addition, expression of the sRNA at a distal site on the gonococcal chromosome in the context of a promoter mutant did not support pilin Av. We conclude that the DNA containing the G-rich sequence can only form the G4 structure during transcription of this sRNA, thus providing a unique molecular step for the initiation of programmed recombination events.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Comment in
-
Bacterial pathogenesis: sRNA clears the way for G4.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013 Mar;11(3):146. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2985. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23411855 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Neisseria gonorrhoeae MutS affects pilin antigenic variation through mismatch correction and not by pilE guanine quartet binding.J Bacteriol. 2015 May;197(10):1828-38. doi: 10.1128/JB.02594-14. Epub 2015 Mar 16. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25777677 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional initiation of a small RNA, not R-loop stability, dictates the frequency of pilin antigenic variation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae.Mol Microbiol. 2019 Oct;112(4):1219-1234. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14356. Epub 2019 Aug 8. Mol Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31338863 Free PMC article.
-
Neisseria gonorrhoeae RecQ helicase HRDC domains are essential for efficient binding and unwinding of the pilE guanine quartet structure required for pilin antigenic variation.J Bacteriol. 2013 May;195(10):2255-61. doi: 10.1128/JB.02217-12. Epub 2013 Mar 8. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23475972 Free PMC article.
-
Pilin gene variation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae: reassessing the old paradigms.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2009 May;33(3):521-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2009.00171.x. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19396954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Focusing homologous recombination: pilin antigenic variation in the pathogenic Neisseria.Mol Microbiol. 2011 Sep;81(5):1136-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07773.x. Epub 2011 Aug 4. Mol Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21812841 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Loop structures in the 5' untranslated region and antisense RNA mediate pilE gene expression in Neisseria gonorrhoeae.Microbiology (Reading). 2016 Nov;162(11):2005-2016. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000369. Epub 2016 Sep 1. Microbiology (Reading). 2016. PMID: 27590250 Free PMC article.
-
R-loops modulate Trypanosome antigenic variation.PLoS Genet. 2018 Dec 13;14(12):e1007809. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007809. eCollection 2018 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 30543632 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Altering the Neisseria gonorrhoeae pilE Guanine Quadruplex Loop Bases Affects Pilin Antigenic Variation.Biochemistry. 2020 Mar 17;59(10):1104-1112. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b01038. Epub 2020 Feb 27. Biochemistry. 2020. PMID: 32078293 Free PMC article.
-
Activity of Bdellovibrio hit locus proteins, Bd0108 and Bd0109, links Type IVa pilus extrusion/retraction status to prey-independent growth signalling.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 5;8(11):e79759. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079759. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24224002 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a novel antisense RNA in the major pilin locus of Neisseria meningitidis influencing antigenic variation.J Bacteriol. 2015 May;197(10):1757-68. doi: 10.1128/JB.00082-15. Epub 2015 Mar 9. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25755192 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cohen MS, Cannon JG (1999) Human experimentation with Neisseria gonorrhoeae: progress and goals. J Infect Dis 179 Suppl 2: S375–379. - PubMed
-
- Park HS, Wolfgang M, van Putten JP, Dorward D, Hayes SF, et al. (2001) Structural alterations in a type IV pilus subunit protein result in concurrent defects in multicellular behaviour and adherence to host tissue. Mol Microbiol 42: 293–307. - PubMed
-
- Rudel T, van Putten JP, Gibbs CP, Haas R, Meyer TF (1992) Interaction of two variable proteins (PilE and PilC) required for pilus-mediated adherence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to human epithelial cells. Mol Microbiol 6: 3439–3450. - PubMed
-
- Wolfgang M, Lauer P, Park HS, Brossay L, Hebert J, et al. (1998) PilT mutations lead to simultaneous defects in competence for natural transformation and twitching motility in piliated Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Mol Microbiol 29: 321–330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

