Efficient and comprehensive representation of uniqueness for next-generation sequencing by minimum unique length analyses
- PMID: 23349747
- PMCID: PMC3548888
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053822
Efficient and comprehensive representation of uniqueness for next-generation sequencing by minimum unique length analyses
Abstract
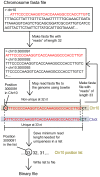
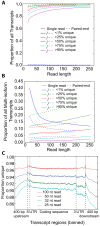
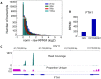
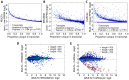
As next generation sequencing technologies are getting more efficient and less expensive, RNA-Seq is becoming a widely used technique for transcriptome studies. Computational analysis of RNA-Seq data often starts with the mapping of millions of short reads back to the genome or transcriptome, a process in which some reads are found to map equally well to multiple genomic locations (multimapping reads). We have developed the Minimum Unique Length Tool (MULTo), a framework for efficient and comprehensive representation of mappability information, through identification of the shortest possible length required for each genomic coordinate to become unique in the genome and transcriptome. Using the minimum unique length information, we have compared different uniqueness compensation approaches for transcript expression level quantification and demonstrate that the best compensation is achieved by discarding multimapping reads and correctly adjusting gene model lengths. We have also explored uniqueness within specific regions of the mouse genome and enhancer mapping experiments. Finally, by making MULTo available to the community we hope to facilitate the use of uniqueness compensation in RNA-Seq analysis and to eliminate the need to make additional mappability files.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
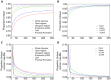
References
-
- Metzker ML (2010) Sequencing technologies - the next generation. Nature Reviews Genetics 11: 31–46 Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19997069. - PubMed
-
- Mortazavi A, Williams B, McCue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B (2008) Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods Available: http://www.nature.com/nmeth/journal/vaop/ncurrent/abs/nmeth.1226.html. - PubMed
-
- Wang ET, Sandberg R, Luo S, Khrebtukova I, Zhang L, et al. (2008) Alternative isoform regulation in human tissue transcriptomes. Nature 456: 470–476 Available: http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v456/n7221/abs/nature07509.html. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pan Q, Shai O, Lee LJ, Frey BJ, Blencowe BJ (2008) Deep surveying of alternative splicing complexity in the human transcriptome by high-throughput sequencing. Nature Genetics 40: 1413–1415 Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18978789. - PubMed
-
- Lee S, Seo CH, Lim B, Yang JO, Oh J, et al. (2011) Accurate quantification of transcriptome from RNA-Seq data by effective length normalization. Nucleic Acids Research 39: e9 Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21059678. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

