p68/DdX5 supports β-catenin & RNAP II during androgen receptor mediated transcription in prostate cancer
- PMID: 23349811
- PMCID: PMC3547877
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054150
p68/DdX5 supports β-catenin & RNAP II during androgen receptor mediated transcription in prostate cancer
Abstract
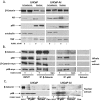
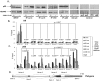
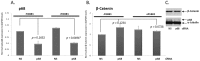
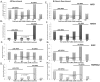
The DEAD box RNA helicase p68 (Ddx5) is an important androgen receptor (AR) transcriptional co-activator in prostate cancer (PCa) and is over-expressed in late stage disease. β-Catenin is a multifunctional protein with important structural and signalling functions which is up-regulated in PCa and similar to p68, interacts with the AR to co-activate expression of AR target genes. Importantly, p68 forms complexes with nuclear β-Catenin and promotes gene transcription in colon cancer indicating a functional interplay between these two proteins in cancer progression. In this study, we explore the relationship of p68 and β-Catenin in PCa to assess their potential co-operation in AR-dependent gene expression, which may be of importance in the development of castrate resistant prostate cancer (CRPCa). We use immunoprecipitation to demonstrate a novel interaction between p68 and β-Catenin in the nucleus of PCa cells, which is androgen dependent in LNCaP cells but androgen independent in a hormone refractory derivative of the same cell line (representative of the CRPCa disease type). Enhanced AR activity is seen in androgen-dependent luciferase reporter assays upon transient co-transfection of p68 and β-Catenin as an additive effect, and p68-depleted Chromatin-Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) showed a decrease in the recruitment of the AR and β-Catenin to androgen responsive promoter regions. In addition, we found p68 immunoprecipitated with the processive and non-processive form of RNA polymerase II (RNAP II) and show p68 recruited to elongating regions of the AR mediated PSA gene, suggesting a role for p68 in facilitating RNAP II transcription of AR mediated genes. These results suggest p68 is important in facilitating β-Catenin and AR transcriptional activity in PCa cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The RNA helicase p68 is a novel androgen receptor coactivator involved in splicing and is overexpressed in prostate cancer.Cancer Res. 2008 Oct 1;68(19):7938-46. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0932. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18829551 Free PMC article.
-
DEAD-box protein p68 is regulated by β-catenin/transcription factor 4 to maintain a positive feedback loop in control of breast cancer progression.Breast Cancer Res. 2014 Dec 12;16(6):496. doi: 10.1186/s13058-014-0496-5. Breast Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25499975 Free PMC article.
-
FOXM1 promotes the progression of prostate cancer by regulating PSA gene transcription.Oncotarget. 2017 Mar 7;8(10):17027-17037. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15224. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28199985 Free PMC article.
-
Coupling transcription to RNA processing via the p68 DEAD box RNA helicase androgen receptor co-activator in prostate cancer.Biochem Soc Trans. 2008 Jun;36(Pt 3):546-7. doi: 10.1042/BST0360546. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008. PMID: 18482004 Review.
-
Androgen receptor signaling and mutations in prostate cancer.Asian J Androl. 2010 Sep;12(5):639-57. doi: 10.1038/aja.2010.89. Epub 2010 Aug 16. Asian J Androl. 2010. PMID: 20711217 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lead DEAD/H box helicase biomarkers with the therapeutic potential identified by integrated bioinformatic approaches in lung cancer.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020 Dec 28;19:261-278. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.12.007. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020. PMID: 33425256 Free PMC article.
-
Next-generation sequencing of advanced prostate cancer treated with androgen-deprivation therapy.Eur Urol. 2014 Jul;66(1):32-9. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2013.08.011. Epub 2013 Aug 14. Eur Urol. 2014. PMID: 24054872 Free PMC article.
-
SWATH-MS Based Proteomic Profiling of Prostate Cancer Cells Reveals Adaptive Molecular Mechanisms in Response to Anti-Androgen Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 9;13(4):715. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040715. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33572476 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of DEAD box RNA helicases DDX5 and DDX17 in chromatin organization and transcriptional regulation.BMB Rep. 2018 Dec;51(12):613-622. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2018.51.12.234. BMB Rep. 2018. PMID: 30293550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DEAD-box RNA helicases with special reference to p68: Unwinding their biology, versatility, and therapeutic opportunity in cancer.Genes Dis. 2022 Mar 21;10(4):1220-1241. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2022.02.008. eCollection 2023 Jul. Genes Dis. 2022. PMID: 37397539 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Feldman BJ, Feldman D (2001) The development of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 1: 34–45. - PubMed
-
- Chen CD, Welsbie DS, Tran C, Baek SH, Chen R, et al. (2004) Molecular determinants of resistance to antiandrogen therapy. Nat Med 10: 33–39. - PubMed
-
- Gordon MD, Nusse R (2006) Wnt signaling: multiple pathways, multiple receptors, and multiple transcription factors. J Biol Chem 281: 22429–22433. - PubMed
-
- Clevers H (2006) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell 127: 469–480. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

