A lectin with highly potent inhibitory activity toward breast cancer cells from edible tubers of Dioscorea opposita cv. nagaimo
- PMID: 23349827
- PMCID: PMC3549954
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054212
A lectin with highly potent inhibitory activity toward breast cancer cells from edible tubers of Dioscorea opposita cv. nagaimo
Abstract
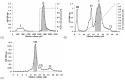
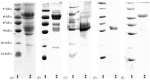
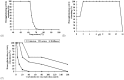
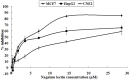
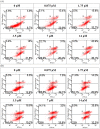
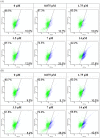
A 70-kDa galactose-specific lectin was purified from the tubers of Dioscorea opposita cv. nagaimo. The purification involved three chromatographic steps: anion exchange chromatography on a Q-Sepharose column, FPLC-anion exchange chromatography on a Mono Q column, and FPLC-gel filtration on a Superdex 75 column. The purified nagaimo lectin presented as a single 35-kDa band in reducing SDS-PAGE while it exhibited a 70-kDa single band in non-reducing SDS-PAGE suggesting its dimeric nature. Nagaimo lectin displayed moderate thermostability, retaining full hemagglutinating activity after heating up to 62°C for 30 minutes. It also manifested stability over a wide pH range from pH 2 to 13. Nagaimo lectin was a galactose-specific lectin, as evidenced by binding with galactose and galactose-containing sugars such as lactose and raffinose. The minimum concentration of galactose, lactose and raffinose required to exert an inhibitory effect on hemagglutinating activity of nagaimo lectin was 20 mM, 5 mM and 40 mM, respectively. Nagaimo lectin inhibited the growth of some cancer cell lines including breast cancer MCF7 cells, hepatoma HepG2 cells and nasopharyngeal carcinoma CNE2 cells, with IC(50) values of 3.71 µM, 7.12 µM and 19.79 µM, respectively, after 24 hour treatment with nagaimo lectin. The induction of phosphatidylserine externalization and mitochondrial depolarization indicated that nagaimo lectin evoked apoptosis in MCF7 cells. However, the anti-proliferative activity of nagaimo lectin was not blocked by application of galactose, signifying that the activity was not related to the carbohydrate binding specificity of the lectin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

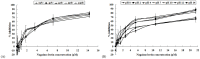
Similar articles
-
Isolation and characterization of a lectin from Japanese mottled beans.Protein Pept Lett. 2014 Jul;21(7):696-704. doi: 10.2174/0929866521666140320100308. Protein Pept Lett. 2014. PMID: 24654854
-
Isolation of a glucosamine binding leguminous lectin with mitogenic activity towards splenocytes and anti-proliferative activity towards tumor cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38961. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038961. Epub 2012 Jun 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22720002 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and characterization of a lectin with potentially exploitable activities from caper (Capparis spinosa) seeds.Biosci Rep. 2009 Jun 15;29(5):293-9. doi: 10.1042/BSR20080110. Biosci Rep. 2009. PMID: 18847434
-
Purification and characterization of a galactose-specific lectin with mitogenic activity from pinto beans.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 May;1760(5):808-13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2006.02.015. Epub 2006 Mar 23. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16600511
-
A hemagglutinin from northeast red beans with immunomodulatory activity and anti-proliferative and apoptosis-inducing activities toward tumor cells.Protein Pept Lett. 2013 Oct;20(10):1159-69. doi: 10.2174/0929866511320100011. Protein Pept Lett. 2013. PMID: 23514011 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification and Validation of Reference Genes for qRT-PCR Studies of Gene Expression in Dioscorea opposita.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:3089584. doi: 10.1155/2016/3089584. Epub 2016 May 26. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27314014 Free PMC article.
-
A Frontier Review of Nutraceutical Chinese Yam.Foods. 2024 May 7;13(10):1426. doi: 10.3390/foods13101426. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38790726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Two-Step Feature Selection Method to Predict Cancerlectins by Multiview Features and Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Feb 7;2018:9364182. doi: 10.1155/2018/9364182. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29568772 Free PMC article.
-
The Dioscorea Genus (Yam)-An Appraisal of Nutritional and Therapeutic Potentials.Foods. 2020 Sep 16;9(9):1304. doi: 10.3390/foods9091304. Foods. 2020. PMID: 32947880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The contents of heavy metals (cd, cr, as, pb, ni, and sn) in the selected commercial yam powder products in South Korea.Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2013 Dec;18(4):249-55. doi: 10.3746/pnf.2013.18.4.249. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2013. PMID: 24551826 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Naeem A, Ahmad E, Ashraf MT, Khan RH (2007) Purification and characterization of mannose/glucose-specific lectin from seeds of Trigonella foenumgraecum. Biochemistry (Mosc) 72: 44–48. - PubMed
-
- Tsivileva OM, Nikitina VE, Loshchinina EA (2007) Isolation and characterization of Lentinus edodes (Berk.) singer extracellular lectins. Biochemistry (Mosc) 73: 1154–1161. - PubMed
-
- Ellgaard L, Frickel EM (2003) Calnexin, calreticulin, and ERp57: teammates in glycoprotein folding. Cell Biochem Biophys 39: 223–247. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

