Wdr68 requires nuclear access for craniofacial development
- PMID: 23349862
- PMCID: PMC3551808
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054363
Wdr68 requires nuclear access for craniofacial development
Abstract
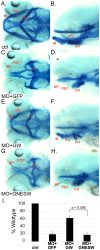
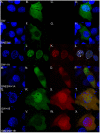
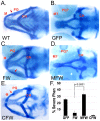
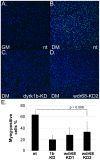
Wdr68 is a highly conserved scaffolding protein required for craniofacial development and left-right asymmetry. A Ras-Map3k-Wdr68-Dyrk1 signaling relay may mediate these and other diverse signaling events important in development and disease. While the sub-cellular localization of Wdr68 has been shown to be dependent on that of its interaction partners, it is not clear where Wdr68 activity is required during development. Here we show that while a GFP-Wdr68 fusion functionally substituted for craniofacial development in the zebrafish, that a Nuclear Export Signal (NES) fusion protein (GFPNESWdr68) failed to support craniofacial development. As control for NES activity, we show that while GFP-Wdr68 exhibited a pan-cellular distribution in C2C12 cells, the GFPNESWdr68 fusion predominantly localized to the cell cytoplasm, as expected. Interestingly, while GFP-Wdr68 and RFP-Dyrk1a co-localized to the cell nucleus as expected based on the known sub-cellular localization for Dyrk1a, we found that the GFPNESWdr68 fusion redistributed RFP-Dyrk1a to the cell cytoplasm potentially disconnecting the Ras/Dyrk1 signal relay from further downstream targets. Consistent with a nuclear role in gene regulation, we also found that while a transcriptional activation domain fusion, CebpFlagWdr68, functionally substituted for endogenous Wdr68 for craniofacial development, that a transcriptional repression domain fusion, MadFlagWdr68, failed to support craniofacial development. Dyrk1b is required for myogenin (myog) expression in differentiating mouse C2C12 cells and here we report that wdr68 is also important for myog expression in differentiating C2C12 cells. Using a C2C12 cell myog promoter-reporter system, we found that Wdr68 overexpression increased reporter activity while moderate expression levels of MadFlagWdr68 interfered with reporter activity. Taken together, these findings support a nuclear role for Wdr68-containing complexes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Wdr68 Mediates Dorsal and Ventral Patterning Events for Craniofacial Development.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 23;11(11):e0166984. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166984. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27880803 Free PMC article.
-
DCAF7/WDR68 is required for normal levels of DYRK1A and DYRK1B.PLoS One. 2018 Nov 29;13(11):e0207779. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207779. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30496304 Free PMC article.
-
A zebrafish screen for craniofacial mutants identifies wdr68 as a highly conserved gene required for endothelin-1 expression.BMC Dev Biol. 2006 Jun 7;6:28. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-6-28. BMC Dev Biol. 2006. PMID: 16759393 Free PMC article.
-
The zebrafish dyrk1b gene is important for endoderm formation.Genesis. 2010 Jan;48(1):20-30. doi: 10.1002/dvg.20578. Genesis. 2010. PMID: 20014342 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic up-regulation of muscle LIM protein expression in C2C12 and NIH3T3 cells by myogenin and MEF2C.Mol Genet Genomics. 2009 Jan;281(1):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s00438-008-0393-7. Epub 2008 Nov 6. Mol Genet Genomics. 2009. PMID: 18987887 Review.
Cited by
-
De novo missense variants in PPP2R5D are associated with intellectual disability, macrocephaly, hypotonia, and autism.Neurogenetics. 2016 Jan;17(1):43-9. doi: 10.1007/s10048-015-0466-9. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Neurogenetics. 2016. PMID: 26576547 Free PMC article.
-
Wdr68 Mediates Dorsal and Ventral Patterning Events for Craniofacial Development.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 23;11(11):e0166984. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166984. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27880803 Free PMC article.
-
DCAF7/WDR68 is required for normal levels of DYRK1A and DYRK1B.PLoS One. 2018 Nov 29;13(11):e0207779. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207779. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30496304 Free PMC article.
-
The adaptor protein DCAF7 mediates the interaction of the adenovirus E1A oncoprotein with the protein kinases DYRK1A and HIPK2.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 16;6:28241. doi: 10.1038/srep28241. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27307198 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-Specificity, Tyrosine Phosphorylation-Regulated Kinases (DYRKs) and cdc2-Like Kinases (CLKs) in Human Disease, an Overview.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 3;22(11):6047. doi: 10.3390/ijms22116047. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34205123 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- de Vetten N, Quattrocchio F, Mol J, Koes R (1997) The an11 locus controlling flower pigmentation in petunia encodes a novel WD-repeat protein conserved in yeast, plants, and animals. Genes Dev 11: 1422–1434. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

