Neural progenitor cell implants modulate vascular endothelial growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in rat axotomized neurons
- PMID: 23349916
- PMCID: PMC3548797
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054519
Neural progenitor cell implants modulate vascular endothelial growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in rat axotomized neurons
Abstract
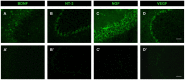
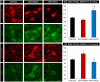
Axotomy of central neurons leads to functional and structural alterations which largely revert when neural progenitor cells (NPCs) are implanted in the lesion site. The new microenvironment created by NPCs in the host tissue might modulate in the damaged neurons the expression of a high variety of molecules with relevant roles in the repair mechanisms, including neurotrophic factors. In the present work, we aimed to analyze changes in neurotrophic factor expression in axotomized neurons induced by NPC implants. For this purpose, we performed immunofluorescence followed by confocal microscopy analysis for the detection of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) and nerve growth factor (NGF) on brainstem sections from rats with axotomy of abducens internuclear neurons that received NPC implants (implanted group) or vehicle injections (axotomized group) in the lesion site. Control abducens internuclear neurons were strongly immunoreactive to VEGF and BDNF but showed a weak staining for NT-3 and NGF. Comparisons between groups revealed that lesioned neurons from animals that received NPC implants showed a significant increase in VEGF content with respect to animals receiving vehicle injections. However, the immunoreactivity for BDNF, which was increased in the axotomized group as compared to control, was not modified in the implanted group. The modifications induced by NPC implants on VEGF and BDNF content were specific for the population of axotomized abducens internuclear neurons since the neighboring abducens motoneurons were not affected. Similar levels of NT-3 and NGF immunolabeling were obtained in injured neurons from axotomized and implanted animals. Among all the analyzed neurotrophic factors, only VEGF was expressed by the implanted cells in the lesion site. Our results point to a role of NPC implants in the modulation of neurotrophic factor expression by lesioned central neurons, which might contribute to the restorative effects of these implants.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Titmus MJ, Faber DS (1990) Axotomy-induced alterations in the electrophysiological characteristics of neurons. Prog Neurobiol 35: 1–51. - PubMed
-
- Pastor AM, Delgado-García JM, Martínez-Guijarro FJ, López-García C, de la Cruz RR (2000) Response of abducens internuclear neurons to axotomy in the adult cat. J Comp Neurol 427: 370–390. - PubMed
-
- Giehl KM, Tetzlaff W (1996) BDNF and NT-3, but not NGF, prevent axotomy-induced death of rat corticospinal neurons in vivo. Eur J Neurosci 8: 1167–1175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

