What is the cost of diagnosis and management of drug resistant tuberculosis in South Africa?
- PMID: 23349933
- PMCID: PMC3548831
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054587
What is the cost of diagnosis and management of drug resistant tuberculosis in South Africa?
Abstract
Background: Drug-resistant tuberculosis (DR-TB) is undermining TB control in South Africa. However, there are hardly any data about the cost of treating DR-TB in high burden settings despite such information being quintessential for the rational planning and allocation of resources by policy-makers, and to inform future cost-effectiveness analyses.
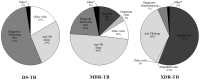
Methodology: We analysed the comparative 2011 United States dollar ($) cost of diagnosis and treatment of drug sensitive TB (DS-TB), MDR-TB and XDR-TB, based on National South African TB guidelines, from the perspective of the National TB Program using published clinical outcome data.
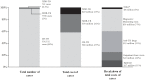
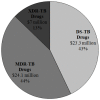
Principal findings: Assuming adherence to national DR-TB management guidelines, the per patient cost of XDR-TB was $26,392, four times greater than MDR-TB ($6772), and 103 times greater than drug-sensitive TB ($257). Despite DR-TB comprising only 2.2% of the case burden, it consumed ~32% of the total estimated 2011 national TB budget of US $218 million. 45% and 25% of the DR-TB costs were attributed to anti-TB drugs and hospitalization, respectively. XDR-TB consumed 28% of the total DR-TB diagnosis and treatment costs. Laboratory testing and anti-TB drugs comprised the majority (71%) of MDR-TB costs while hospitalization and anti-TB drug costs comprised the majority (92%) of XDR-TB costs. A decentralized XDR-TB treatment programme could potentially reduce costs by $6930 (26%) per case and reduce the total amount spent on DR-TB by ~7%.
Conclusion/significance: Although DR-TB forms a very small proportion of the total case burden it consumes a disproportionate and substantial amount of South Africa's total annual TB budget. These data inform rational resource allocation and selection of management strategies for DR-TB in high burden settings.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (2011) WHO Report 2011: Global Tuberculosis Control. (2011) Available: http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/. Accessed 2012 Oct 20.
-
- United Nations (2011) The UN Millenium Development Goals Report 2011 (2011) Available: www.un.org/millenniumgoals/reports.shtml.Accessed 2012 Mar.
-
- Dheda K, Migliori GB (2012) The global rise of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis: is the time to bring back sanatoria now overdue? Lancet 379: 773–775. - PubMed
-
- Dheda K, Warren RM, Zumla A, Grobusch MP (2010) Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis: epidemiology and management challenges. Infect Dis Clin North Am 24: 705–725. - PubMed
-
- South African Department of Health (2011) Management of Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis: Policy Guidelines (2011) Available: www.kznhealth.gov.za/pharmacy/ptc/MDR2011.pdf.Accessed 2012 Oct 3.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

