In silico identification of IgE-binding epitopes of osmotin protein
- PMID: 23349964
- PMCID: PMC3548786
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054755
In silico identification of IgE-binding epitopes of osmotin protein
Abstract
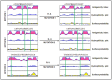
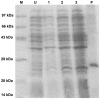
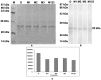
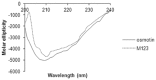
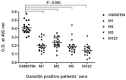
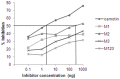
The identification of B-cell epitopes is an important step to study the antigen- antibody interactions for diagnosis and therapy. The present study aimed to identify B- cell epitopes of osmotin using bioinformatic tools and further modify these regions to study the allergenic property. B-cell epitopes were predicted based on amino acid physicochemical properties. Three single point mutations M1, M2, and M3 and a multiple point mutant (M123) were selected to disrupt the IgE binding. These mutants were cloned, expressed and proteins purified to homogeneity. The IgE binding of the purified proteins was evaluated by ELISA and ELISA inhibition with patients' sera. Three regions of osmotin M1 (57-70 aa), M2 (72-85 aa) and M3 (147-165 aa) were identified as potential antibody recognition sites using in silico tools. The sequence similarity search of the predicted epitopes of osmotin using Structural Database of Allergenic proteins (SDAP) showed similarity with known allergens from tomato, kiwifruit, bell pepper, apple, mountain cedar and cypress. Mutants M1, M2 and M3 showed up to 72%, 60% and 76% reduction, respectively in IgE binding whereas M123 showed up to 90% reduction with patients' sera. The immunoblot of M123 mutant showed 40% reduction in spot density as compared to osmotin. All mutants showed decreased inhibition potency with M123 exhibiting lowest potency of 32% with osmotin positive pooled patients' sera. The three B- cell epitopes of osmotin predicted by in silico method correlated with the experimental approach. The mutant M123 showed a reduction of 90% in IgE binding. The present method may be employed for prediction of B- cell epitopes of allergenic proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Cianferoni A, Spergel JM (2009) Food allergy: review, classification and diagnosis. Allergol Int 58: 457–466. - PubMed
-
- Vrtala S (2008) From allergen genes to new forms of allergy diagnosis and treatment. Allergy 63: 299–309. - PubMed
-
- Nelson HS, Lahr J, Rule R, Bock A, Leung D (1997) Treatment of anaphylactic sensitivity to peanuts by immunotherapy with injections of aqueous peanut extract. J Allergy Clin Immunol 99: 744–751. - PubMed
-
- Reese G, Viebranz J, Leong-Kee SM, Plante M, Lauer I, et al. (2005) Reduced Allergenic Potency of VR9-1, a Mutant of the Major Shrimp Allergen Pen a 1 (Tropomyosin). J Immunol 175: 8354–8364. - PubMed
-
- Toda M, Reese G, Gadermaier G, Schulten V, Lauer I, et al. (2011) Protein unfolding strongly modulates the allergenicity and immunogenicity of Pru p 3, the major peach allergen. J Allergy Clin Immunol 128: 1022–1030. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

