Women with multiple chemical sensitivity have increased harm avoidance and reduced 5-HT(1A) receptor binding potential in the anterior cingulate and amygdala
- PMID: 23349968
- PMCID: PMC3551905
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054781
Women with multiple chemical sensitivity have increased harm avoidance and reduced 5-HT(1A) receptor binding potential in the anterior cingulate and amygdala
Abstract
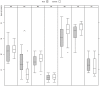
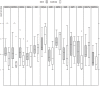
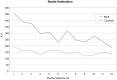
Multiple chemical sensitivity (MCS) is a common condition, characterized by somatic distress upon exposure to odors. As in other idiopathic environmental intolerances, the underlying mechanisms are unknown. Contrary to the expectations it was recently found that persons with MCS activate the odor-processing brain regions less than controls, while their activation of the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) is increased. The present follow-up study was designed to test the hypotheses that MCS subjects have increased harm avoidance and deviations in the serotonin system, which could render them intolerant to environmental odors. Twelve MCS and 11 control subjects, age 22-44, all working or studying females, were included in a PET study where 5-HT(1A) receptor binding potential (BP) was assessed after bolus injection of [(11)C]WAY100635. Psychological profiles were assessed by the Temperament and Character Inventory and the Swedish universities Scales of Personality. All MCS and 12 control subjects were also tested for emotional startle modulation in an acoustic startle test. MCS subjects exhibited significantly increased harm avoidance, and anxiety compared to controls. They also had a reduced 5-HT(1A) receptor BP in amygdala (p = 0.029), ACC (p = 0.005) (planned comparisons, significance level 0.05), and insular cortex (p = 0.003; significance level p<0.005 with Bonferroni correction), and showed an inverse correlation between degree of anxiety and the BP in the amygdala (planned comparison). No group by emotional category difference was found in the startle test. Increased harm avoidance and the observed changes in the 5-HT(1A) receptor BP in the regions processing harm avoidance provides a plausible pathophysiological ground for the symptoms described in MCS, and yields valuable information for our general understanding of idiopathic environmental intolerances.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chronic stress is linked to 5-HT(1A) receptor changes and functional disintegration of the limbic networks.Neuroimage. 2011 Apr 1;55(3):1178-88. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.12.060. Epub 2011 Jan 4. Neuroimage. 2011. PMID: 21211567
-
Behavioral depression and positron emission tomography-determined serotonin 1A receptor binding potential in cynomolgus monkeys.Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006 Apr;63(4):396-403. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.63.4.396. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006. PMID: 16585468
-
Influence of escitalopram treatment on 5-HT 1A receptor binding in limbic regions in patients with anxiety disorders.Mol Psychiatry. 2009 Nov;14(11):1040-50. doi: 10.1038/mp.2008.35. Epub 2008 Mar 25. Mol Psychiatry. 2009. PMID: 18362913
-
Serotonin-1A receptor alterations in depression: a meta-analysis of molecular imaging studies.BMC Psychiatry. 2016 Sep 13;16(1):319. doi: 10.1186/s12888-016-1025-0. BMC Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27623971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Pathophysiology of multiple chemical sensitivity].Rev Mal Respir. 2013 Jun;30(6):446-50. doi: 10.1016/j.rmr.2013.02.016. Epub 2013 Apr 18. Rev Mal Respir. 2013. PMID: 23835316 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Perceptual Sensitivity and Response to Strong Stimuli Are Related.Front Psychol. 2017 Sep 22;8:1642. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01642. eCollection 2017. Front Psychol. 2017. PMID: 29018377 Free PMC article.
-
Left and right amygdala - mediofrontal cortical functional connectivity is differentially modulated by harm avoidance.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 23;9(4):e95740. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095740. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24760033 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Chemical Sensitivity: A Clinical Perspective.Brain Sci. 2024 Dec 16;14(12):1261. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14121261. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 39766460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psychological symptoms and self-image of patients with complaints attributed to dental restorative materials.Clin Oral Investig. 2019 Jun;23(6):2805-2811. doi: 10.1007/s00784-018-2707-4. Epub 2018 Oct 27. Clin Oral Investig. 2019. PMID: 30368660
-
Changes in cerebral blood flow during olfactory stimulation in patients with multiple chemical sensitivity: a multi-channel near-infrared spectroscopic study.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 21;8(11):e80567. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080567. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24278291 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kreutzer R, Neutra RR, Lashuay N (1999) Prevalence of people reporting sensitivities to chemicals in a population-based survey. Am J Epidemiol 150: 1–12. - PubMed
-
- Meggs WJ, Dunn KA, Bloch RM, Goodman PE (1996) Prevalence and nature of allergy and chemical sensitivity in a general population. Arch Environ Health 51: 275–282. - PubMed
-
- Berg ND, Linneberg A, Dirksen A, Elberling J (2008) Prevalence of self-reported symptoms and consequences related to inhalation of airborne chemicals in a Danish general population. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 81: 881–887. - PubMed
-
- Cullen MR (1987) The worker with multiple chemical sensitivities. Occup Med 2: 655–661. - PubMed
-
- Anonymous (1999) Multiple chemical sensitivity: a 1999 consensus. Arch Environ Health 54: 147–149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

