Environmental enrichment and gut inflammation modify stress-induced c-Fos expression in the mouse corticolimbic system
- PMID: 23349972
- PMCID: PMC3547954
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054811
Environmental enrichment and gut inflammation modify stress-induced c-Fos expression in the mouse corticolimbic system
Abstract
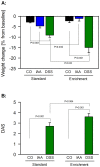
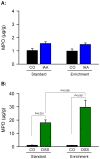
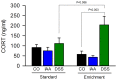
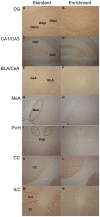
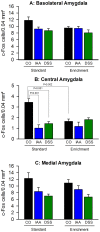
Environmental enrichment (EE) has a beneficial effect on rodent behaviour, neuronal plasticity and brain function. Although it may also improve stress coping, it is not known whether EE influences the brain response to an external (psychological) stressor such as water avoidance stress (WAS) or an internal (systemic) stressor such as gastrointestinal inflammation. This study hence explored whether EE modifies WAS-induced activation of the mouse corticolimbic system and whether this stress response is altered by gastritis or colitis. Male C67BL/6N mice were housed under standard or enriched environment for 9 weeks, after which they were subjected to a 1-week treatment with oral iodoacetamide to induce gastritis or oral dextran sulfate sodium to induce colitis. Following exposure to WAS the expression of c-Fos, a marker of neuronal activation, was measured by immunocytochemistry. EE aggravated experimentally induced colitis, but not gastritis, as shown by an increase in the disease activity score and the colonic myeloperoxidase content. In the brain, EE enhanced the WAS-induced activation of the dentate gyrus and unmasked an inhibitory effect of gastritis and colitis on WAS-evoked c-Fos expression within this part of the hippocampus. Conversely, EE inhibited the WAS-evoked activation of the central amygdala and prevented the inhibitory effect of gastritis and colitis on WAS-evoked c-Fos expression in this region. EE, in addition, blunted the WAS-induced activation of the infralimbic cortex and attenuated the inhibitory effect of gastritis and colitis on WAS-evoked c-Fos expression in this area. These data reveal that EE has a region-specific effect on stress-induced c-Fos expression in the corticolimbic system, which is likely to improve stress resilience. The response of the prefrontal cortex - amygdala - hippocampus circuitry to psychological stress is also modified by the systemic stress of gut inflammation, and this interaction between external and internal stressors is modulated by the housing environment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Differential impact of stress and environmental enrichment on corticolimbic circuits.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2020 Oct;197:172993. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2020.172993. Epub 2020 Jul 11. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2020. PMID: 32659243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis alters stress-associated behaviour and neuropeptide gene expression in the amygdala-hippocampus network of mice.Sci Rep. 2015 Jun 12;5:9970. doi: 10.1038/srep09970. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26066467 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental enrichment confers stress resiliency to social defeat through an infralimbic cortex-dependent neuroanatomical pathway.J Neurosci. 2011 Apr 20;31(16):6159-73. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0577-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21508240 Free PMC article.
-
Increase in gastric acid-induced afferent input to the brainstem in mice with gastritis.Neuroscience. 2007 Mar 30;145(3):1108-19. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.12.025. Epub 2007 Feb 14. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17303342 Free PMC article.
-
Cardinal role of the environment in stress induced changes across life stages and generations.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021 May;124:137-150. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.01.012. Epub 2021 Feb 4. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021. PMID: 33549740 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ethanol intake in male mice exposed to social defeat: Environmental enrichment potentiates resilience.Neurobiol Stress. 2021 Nov 3;15:100413. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2021.100413. eCollection 2021 Nov. Neurobiol Stress. 2021. PMID: 34815986 Free PMC article.
-
A novel unbiased counting method for the quantification of synapses in the mouse brain.J Neurosci Methods. 2015 Jan 30;240:13-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2014.10.020. Epub 2014 Nov 3. J Neurosci Methods. 2015. PMID: 25445248 Free PMC article.
-
Galanin receptor 3 attenuates inflammation and influences the gut microbiota in an experimental murine colitis model.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 12;11(1):564. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-79456-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33436730 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells of Dental Origin-Their Potential for Antiinflammatory and Regenerative Actions in Brain and Gut Damage.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2016;14(8):914-934. doi: 10.2174/1570159x14666160121115210. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26791480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential impact of stress and environmental enrichment on corticolimbic circuits.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2020 Oct;197:172993. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2020.172993. Epub 2020 Jul 11. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2020. PMID: 32659243 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- van Praag H, Kempermann G, Gage FH (2000) Neural consequences of environmental enrichment. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience 1: 191–198. - PubMed
-
- Leggio MG, Mandolesi L, Federico F, Spirito F, Ricci B, et al. (2005) Environmental enrichment promotes improved spatial abilities and enhanced dendritic growth in the rat. Behavioural Brain Research 163: 78–90. - PubMed
-
- Meshi D, Drew MR, Saxe M, Ansorge MS, David D, et al. (2006) Hippocampal neurogenesis is not required for behavioral effects of environmental enrichment. Nature Neuroscience 9: 729–731. - PubMed
-
- Roy V, Belzung C, Delarue C, Chapillon P (2001) Environmental enrichment in BALB/c mice: Effects in classical tests of anxiety and exposure to a predatory odor. Physiology & Behavior 74: 313–320. - PubMed
-
- Van de Weerd HA, Aarsen EL, Mulder A, Kruitwagen CL, Hendriksen CF, et al. (2002) Effects of environmental enrichment for mice: Variation in experimental results. Journal of Applied Animal Welfare Science: JAAWS 5: 87–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

