Clinical value of NGAL, L-FABP and albuminuria in predicting GFR decline in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients
- PMID: 23349979
- PMCID: PMC3551928
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054863
Clinical value of NGAL, L-FABP and albuminuria in predicting GFR decline in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients
Abstract
Objectives: Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and liver-type fatty acid binding protein (L-FABP) are emerging as excellent biomarkers in the urine and plasma for the early prediction of acute and chronic kidney injury. The aims of this prospective study were to determine the role of albuminuria, and that of serum and urine levels of NGAL and L-FABP as predictors of a decline in the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods: A longitudinal cohort study with one hundred forty type 2 diabetic patients was conducted. Serum and urine levels of NGAL and L-FABP, and the urine albumin excretion rate were determined. The correlation between the kidney injury biomarkers and rate of GFR decline was analyzed.
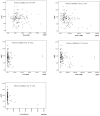
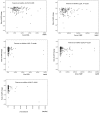
Results: The eGFR of study subjects decreased significantly as the study progressed (86.4±31.1 vs. 74.4±27.3 ml/min/1.73 m(2), P<0.001), and the urine albumin excretion rate increased significantly (264.9±1060.3 vs. 557.7±2092.5 mg/day, P = 0.009). The baseline urine albumin excretion rate and serum L-FABP level were significantly correlated with baseline eGFR (P<0.05). The results of regression analysis for the correlations between the rate of eGFR change and the baseline levels of NGAL and L-FABP, and the urine albumin excretion rate showed that only the urine albumin excretion rate was significantly correlated with the rate of eGFR change (standardized coefficients: -0.378; t: -4.298; P<0.001).
Conclusions: Tubular markers, such as NGAL and L-FABP, may not be predictive factors associated with GFR decline in type 2 diabetic patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Rossing P (2006) Diabetic nephropathy: worldwide epidemic and effects of current treatment on natural history. Curr Diab Rep 6: 479–483. - PubMed
-
- Neilsen SE, Schjoedt KJ, Rossing P (2010) Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalcin (NGAL) and Kidney Injury Molecule (KIM1) in patients with diabetes nephropathy: a cross-sectional study and the effects of lisinopril. Diabet Med 27: 1144–1150. - PubMed
-
- Fioretto P, Steffes MW, Brown DM, Mauer SM (1992) An overview of renal pathology in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in relationship to altered glomerular hemodynamics. Am J Kidney Dis 20: 549–558. - PubMed
-
- Nickolas TL, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2008) Biomarkers in acute and chronic kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 17: 127–132. - PubMed
-
- Dronavalli S, Duka I, Bakris GL (2008) The pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 4: 444–452. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

