Synthesis of long T₁ silicon nanoparticles for hyperpolarized ²⁹Si magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 23350651
- PMCID: PMC3612549
- DOI: 10.1021/nn305462y
Synthesis of long T₁ silicon nanoparticles for hyperpolarized ²⁹Si magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
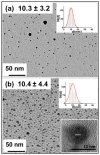
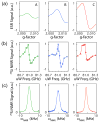
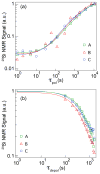
We describe the synthesis, materials characterization, and dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) of amorphous and crystalline silicon nanoparticles for use as hyperpolarized magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) agents. The particles were synthesized by means of a metathesis reaction between sodium silicide (Na₄Si₄) and silicon tetrachloride (SiCl₄) and were surface functionalized with a variety of passivating ligands. The synthesis scheme results in particles of diameter ∼10 nm with long size-adjusted ²⁹Si spin-lattice relaxation (T₁) times (>600 s), which are retained after hyperpolarization by low-temperature DNP.
Figures




References
-
- Wilson WL, Szajowski PF, Brus LE. Quantum Confinement In Size-Selected, Surface-Oxidized Silicon Nanocrystals. Science. 1993;262:1242–1244. - PubMed
-
- Ledoux G, Gong J, Huisken F, Guillois O, Reynaud C. Photoluminescence Of Size-Separated Silicon Nanocrystals: Confirmation Of Quantum Confinement. Appl Phys Lett. 2002;80:4834–4836.
-
- Cullis AG, Canham LT, Calcott PDJ. The Structural And Luminescence Properties Of Porous Silicon. J Appl Phys. 1997;82:909–965.
-
- Tian BZ, Zheng XL, Kempa TJ, Fang Y, Yu NF, Yu GH, Huang JL, Lieber CM. Coaxial Silicon Nanowires As Solar Cells And Nanoelectronic Power Sources. Nature. 2007;449:885–U8. - PubMed
-
- Pillai S, Catchpole KR, Trupke T, Green MA. Surface Plasmon Enhanced Silicon Solar Cells. J Appl Phys. 2007;101:093105.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

