Comparison of hypertonic saline versus normal saline on cytokine profile during CABG
- PMID: 23351427
- PMCID: PMC3555740
- DOI: 10.1186/2008-2231-20-49
Comparison of hypertonic saline versus normal saline on cytokine profile during CABG
Abstract
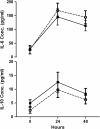
Background and the purpose of the study: Blood contact with artificial surfaces of the extracorporeal circuit and ischemia-reperfusion injury in CABG with CPB, may lead to a systemic inflammatory response. Hypertonic saline have been recently investigated as a fluid in order to decrease inflammatory response and cytokines generation in patients undergo cardiac operations. Our purpose is to study the prophylactic effect of HS 5% infusion versus NS on serum IL-6 as an inflammatory & IL-10 as an anti-inflammatory biomarker in CABG patients.
Methods: The present study is a randomized double-blinded clinical trial. 40 patients undergoing CABG were randomized to receive HS 5% or NS before operation. Blood samples were obtained after receiving HS or NS, just before operation, 24 and 48 hours post-operatively. Plasma levels of IL-6 and IL-10 were measured by ELISA.
Results and major conclusion: Patients received HS had lower levels of IL-6 and higher level of IL-10 compared with NS group, however these differences were not statistically significant. Results of this study suggest that pre-treatment with small volume hypertonic saline 5% may have beneficial effects on inflammatory response following CABG operation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of Hypertonic Saline Infusion versus Normal Saline on Serum NGAL and Cystatin C Levels in Patients Undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Graft.J Tehran Heart Cent. 2013 Jan;8(1):21-7. Epub 2013 Jan 8. J Tehran Heart Cent. 2013. PMID: 23646044 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of 3% hypertonic saline as early fluid resuscitation in pediatric septic shock].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2015 Aug;53(8):599-604. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26717658 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Hypertonic saline for fluid resuscitation in ICU patients post-cardiac surgery (HERACLES): a double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial.Intensive Care Med. 2020 Sep;46(9):1683-1695. doi: 10.1007/s00134-020-06132-0. Epub 2020 Jun 9. Intensive Care Med. 2020. PMID: 32519005 Clinical Trial.
-
Inflammatory activity modulation by hypertonic saline and pentoxifylline in a rat model of strangulated closed loop small bowel obstruction.Int J Surg. 2014;12(6):594-600. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2014.04.007. Epub 2014 May 4. Int J Surg. 2014. PMID: 24797690
-
[Colloidal hypertonic solutions in cardiac surgery].Zentralbl Chir. 1993;118(5):250-6. Zentralbl Chir. 1993. PMID: 7686706 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Prevalence and Risk Factors of Hypoxemia after Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting: The Time to Change Our Conceptions.J Tehran Heart Cent. 2019 Apr;14(2):74-80. J Tehran Heart Cent. 2019. PMID: 31723349 Free PMC article.
-
Causal associations between circulating cytokines and risk of sepsis and related outcomes: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 5;15:1336586. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1336586. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38504987 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Factors for Acute Kidney Injury in Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery Patients Based on the Acute Kidney Injury Network Criteria.J Tehran Heart Cent. 2018 Apr;13(2):52-57. J Tehran Heart Cent. 2018. PMID: 30483313 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of subcutaneous infiltration of 0.5% bupivacaine on post-operative C-reactive protein serum titer after craniotomy surgery.Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2013 Feb;27(1):1-6. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2013. PMID: 23483125 Free PMC article.
-
Hypertonic saline for prevention of delirium in geriatric patients who underwent hip surgery.J Neuroinflammation. 2017 Nov 14;14(1):221. doi: 10.1186/s12974-017-0999-y. J Neuroinflammation. 2017. PMID: 29137628 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Rizoli SB, Rhind SG, Shek PN, Inaba K, Filips D, Tien H, Brenneman F, Rotstein O. The immunomodulatory effects of hypertonic saline resuscitation in patients sustaining traumatic hemorrhagic shock: a randomized, controlled, double-blinded trial. Ann Surg. 2006;243:47–57. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000193608.93127.b1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous