Characterizing biobank organizations in the U.S.: results from a national survey
- PMID: 23351549
- PMCID: PMC3706795
- DOI: 10.1186/gm407
Characterizing biobank organizations in the U.S.: results from a national survey
Abstract
Background: Effective translational biomedical research hinges on the operation of 'biobanks,' repositories that assemble, store, and manage collections of human specimens and related data. Some are established intentionally to address particular research needs; many, however, have arisen opportunistically, in a variety of settings and with a variety of expectations regarding their functions and longevity. Despite their rising prominence, little is known about how biobanks are organized and function beyond simple classification systems (government, academia, industry).
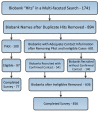
Methods: In 2012, we conducted the first national survey of biobanks in the U.S., collecting information on their origins, specimen collections, organizational structures, and market contexts and sustainability. From a list of 636 biobanks assembled through a multi-faceted search strategy, representatives from 456 U.S. biobanks were successfully recruited for a 30-minute online survey (72% response rate). Both closed and open-ended responses were analyzed using descriptive statistics.
Results: While nearly two-thirds of biobanks were established within the last decade, 17% have been in existence for over 20 years. Fifty-three percent listed research on a particular disease as the most important reason for establishment; 29% listed research generally. Other reasons included response to a grant or gift, and intent to centralize, integrate, or harmonize existing research structures. Biobank collections are extraordinarily diverse in number and types of specimens and in sources (often multiple) from which they are obtained, including from individuals, clinics or hospitals, public health programs, and research studies. Forty-four percent of biobanks store pediatric specimens, and 36% include postmortem specimens. Most biobanks are affiliated in one or multiple ways with other entities: 88% are part of at least one or more larger organizations (67% of these are academic, 23% hospitals, 13% research institutes). The majority of biobanks seem to fill a particular 'niche' within a larger organization or research area; a minority are concerned about competition for services, although many are worried about underutilization of specimens and long-term funding.
Conclusions: Effective utilization of biobank collections and effective policies to govern their use will require understanding of the immense diversity found in organizational features, including the very different history and primary goals that many biobanks have.
Keywords: Biobank; biorepository; governance; survey.
Figures
References
-
- Hoeyer K. Size matters: the ethical, legal, and social issues surrounding large-scale genetic biobank initiatives. Norsk Epidemiologi. 2012;21:211–220.
-
- Fullerton SM, Wolf WA, Brothers KB, Clayton EW, Crawford DC, Denny JC, Greenland P, Koenig BA, Leppig KA, Lindor NM, McCarty CA, McGuire AL, McPeek Hinz ER, Mirel DB, Ramos EM, Ritchie MD, Smith ME, Waudby CJ, Burke W, Jarvik GP. Return of individual research results from genome-wide association studies: experience of the Electronic Medical Records and Genomics (eMERGE) Network. Genet Med. 2012;14:424–431. doi: 10.1038/gim.2012.15. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources