Genetic determinants of cardiometabolic risk: a proposed model for phenotype association and interaction
- PMID: 23351585
- PMCID: PMC3559023
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacl.2012.04.079
Genetic determinants of cardiometabolic risk: a proposed model for phenotype association and interaction
Abstract
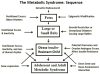
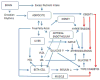
This review provides a translational and unifying summary of metabolic syndrome genetics and highlights evidence that genetic studies are starting to unravel and untangle origins of the complex and challenging cluster of disease phenotypes. The associated genes effectively express in the brain, liver, kidney, arterial endothelium, adipocytes, myocytes, and β cells. Progression of syndrome traits has been associated with ectopic lipid accumulation in the arterial wall, visceral adipocytes, myocytes, and liver. Thus, it follows that the genetics of dyslipidemia, obesity, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease are central in triggering progression of the syndrome to overt expression of disease traits and have become a key focus of interest for early detection and for designing prevention and treatments. To support the "birds' eye view" approach, we provide a road-map depicting commonality and interrelationships between the traits and their genetic and environmental determinants based on known risk factors, metabolic pathways, pharmacologic targets, treatment responses, gene networks, pleiotropy, and association with circadian rhythm. Although only a small portion of the known heritability is accounted for and there is insufficient support for clinical application of gene-based prediction models, there is direction and encouraging progress in a rapidly moving field that is beginning to show clinical relevance.
Copyright © 2013 National Lipid Association. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Mottillo S, Filion KB, Genest J, Joseph L, Pilote L, Poirier P, Rinfret S, Schiffrin EL, Eisenberg MJ. The metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2010;56:1113–32. - PubMed
-
- Morrison JA, Ford ES, Steinberger J. The pediatric metabolic syndrome. Minerva medica. 2008;99:269–87. - PubMed
-
- Wang YZ, Huang YN, Sun KY, Qi JH, Xiang L. Leptin gene transfer regulates fibromuscular development and lipid deposition in muscles via SIRT1, FOXO3a and PGC-1alpha in mice in vivo. International journal of molecular medicine. 2011;28:617–23. - PubMed
-
- Reaven GM. The metabolic syndrome: time to get off the merry-go-round? Journal of internal medicine. 2011;269:127–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

