Identification of human epididymis protein-4 as a fibroblast-derived mediator of fibrosis
- PMID: 23353556
- PMCID: PMC4457508
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.2989
Identification of human epididymis protein-4 as a fibroblast-derived mediator of fibrosis
Abstract
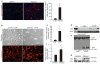
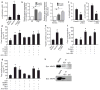
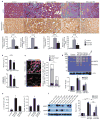
The functional contribution of myofibroblasts in fibrosis is not well understood. Using a new genetic mouse model to track and isolate myofibroblasts, we performed gene expression profiling followed by biological validation to identify HE4 (encoding human epididymis protein 4, also known as WAP 4-disulfide core domain-2 or Wfdc2) as the most upregulated gene in fibrosis-associated myofibroblasts. The HE4 gene encodes for a putative serine protease inhibitor that is upregulated in human and mouse fibrotic kidneys and is elevated in the serum of patients with kidney fibrosis. HE4 suppresses the activity of multiple proteases, including serine proteases and matrix metalloproteinases, and specifically inhibits their capacity to degrade type I collagen. In particular, we identified two serine proteases, Prss35 and Prss23, as HE4 targets with functional relevance in kidney fibrosis. Administration of HE4-neutralizing antibodies accelerated collagen I degradation and inhibited fibrosis in three different mouse models of renal disease. Collectively these studies suggest that HE4 is a potential biomarker of renal fibrosis and a new therapeutic target.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Fibrosis: HE4--a biomarker and target in renal fibrosis.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2013 Mar;9(3):124. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2013.2. Epub 2013 Feb 12. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23399582 No abstract available.
-
Myofibroblasts, regeneration or renal fibrosis--is there a decisive hint?Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013 Nov;28(11):2678-81. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gft247. Epub 2013 Aug 23. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013. PMID: 23975753
References
-
- Zeisberg M, Strutz F, Muller GA. Role of fibroblast activation in inducing interstitial fibrosis. Journal of nephrology. 2000;13 (Suppl 3):S111–120. - PubMed
-
- Eddy AA. Molecular insights into renal interstitial fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1996;7:2495–2508. - PubMed
-
- Strutz F, Muller GA. Renal fibrosis and the origin of the renal fibroblast. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006;21:3368–3370. - PubMed
-
- Okada H, Strutz F, Danoff TM, Kalluri R, Neilson EG. Possible mechanisms of renal fibrosis. Contributions to nephrology. 1996;118:147–154. - PubMed
-
- Zeisberg M, Neilson EG. Mechanisms of tubulointerstitial fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 21:1819–1834. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U54 CA163191/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK55001/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA163191/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA151925/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK081576/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA155370/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32HL007374-30/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007760/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007226/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DK081976/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA151925/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 2T32DK007760-11/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA125550/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA125550/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK055001/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- GM07226/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007374/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA155370/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

